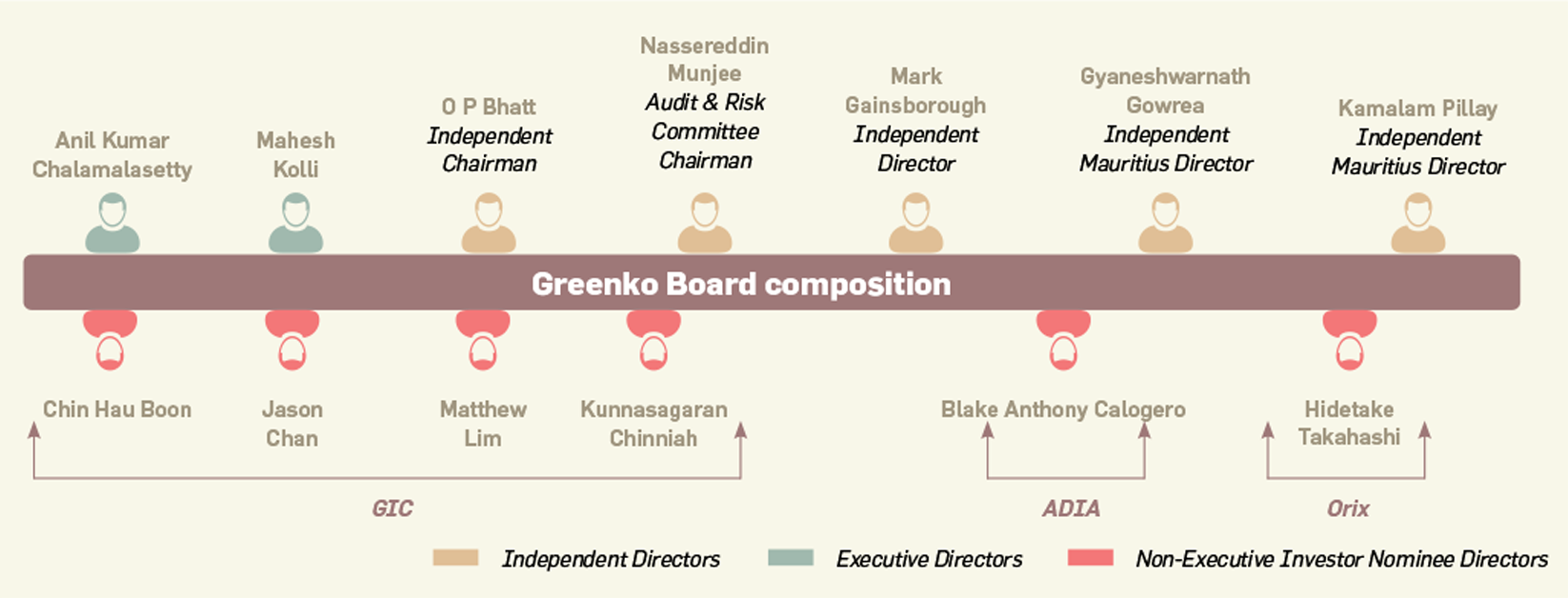
The business operations of Greenko Energy Holdings and its
subsidiaries (Greenko Group) revolve around owning and operating
clean energy technologies in India. The board is constituted by
various representatives from GIC, ADIA, ORIX Founders and
independent directors.
Shareholder Pattern 2
Our
major
stakeholders
GIC,
Sovereign
Wealth
fund of Government
of Singapore and Abu
Dhabi
Investment
Authority
(ADIA),
Sovereign
Wealth
fund of Government
of Abu Dhabi , ORIX
Corporation
and
Greenko
Vetures
Limited.
Greenko has well drafted set of
principles, policies, structures leading
to a strong and resilient corporate
governance framework, that serve
as a nucleus for carrying out the
company’s business operations to
meet
financial,
operational,
and
strategic objectives and also defines
a mutual relationship between its
shareholders, stakeholders and the
Board. By adhering 100% to the
framework, Greenko continues to
enjoy enhanced stakeholder trust year
on year and emerges to be a strong,
viable, competitive and accountable
corporation.
The
governance
framework is crafted considering
- The nature of the business
- The company’s size and stage of development
- Availability of resources
- Shareholder’s expectations and
- Legal and regulatory requirements
The Governance Framework at
Greenko is constructed on the
following principles:
Ethical approach – culture, society;
organizational paradigm
Balanced objectives – congruence
of goals of all interested parties
Each party plays its part – roles
of
key
players:
shareholders/
directors/ staff
Decision-making process in place –
reflecting the first three principles
and giving due weight to all
stakeholders
Equal concern for all stakeholders
– albeit some have greater weight
than others
Accountability and transparency –
for all stakeholders
The salient features of Greenko’s
Corporate Governance Framework are
as follows
Steering for the Long-Term 3
Greenko’s Vision and Mission are well
aligned with the shareholder interests
for accomplishing long term goals. To
continue the focus on decarbonization,
digitalization,
and
decentralization
of the Energy System in India and
harness all the value pools, Greenko
cannot afford to be immobilized by
the demands of quarterly results and
focuses always on long-term goals,
such as market share targets, percent
of revenue from new markets, besides
quarterly earnings guidance. Greenko
follows a staggered representation
of the Board and this ensures in
promoting continuity and stability
across the boardroom.
Best in the Board
Greenko’s Board ensures that its
membership has the proper mix of skills
and perspectives. To reaffirm this, the
Board not only follows age term limits
but also maintains gender and other
diversity requirements. The Board
critically reviews their composition
and appropriate skill sets to promote
ambitious growth of the company.
The Board presently conducts internal evaluations by the chairman or lead
director and process design for reviews
involving grading directors on various
company-specific attributes.
Orderly Voice to Shareholders
Greenko’s
executive
directors’
campaign
aims
to
provide
shareholders equal opportunity to
make decisions and make their voice
heard in a reasonable way.
At Greenko, we follow the best
corporate governance practices, as
stated below:
- The
Board
comprises
of
knowledgeable directors who are
highly qualified and competent,
having
relevant
expertise
in
business operations. They have
strong ethics and integrity, diverse
backgrounds and skillsets, and
sufficient time to commit to their
duties.
- The Board identifies regularly
the gaps in the list of directors,
complement
them
with
ideal
qualities,
characteristics
and
keeps an ‘evergreen’ list of suitable
candidates to fill Board vacancies.
- Most of the directors are non-
executive and some including the
Chairman are independent.
- An
engaged
Board
where
directors’ question and challenge
management decisions.
- Conducting
familiarization
programs covering the business,
their duties, and the Board’s
expectations; reserve time in Board
meetings for ongoing education
about the business and governance
matters.
- Review
Board
mandates
and
undertake performance evaluation.
Define roles and responsibilities
Greenko conventionally adheres to
following good governance principles:
-
Written mandates for the Board
and each committee setting out
their duties and accountabilities.
-
Delegation
of
certain
responsibilities
to
committees
such as audit, nomination, and remuneration and ‘special committees’
formed to evaluate proposed transactions
or opportunities.
-
Written position descriptions for the Board
Chair, Board committees, the CEO, and
executive officers.
-
Separation of the roles of the Board Chair
and the CEO: The Chair leads the Board
and ensures it acts in the company’s long-
term interests; the CEO leads management,
develops and implements business strategy,
and reports to the Board.
Emphasize integrity and ethical dealing
-
Adopted a conflict-of-interest policy and a
code of business conduct setting out the
company’s requirements and process to
report and deal with non-compliance and
formulated a Whistle blower policy.
-
Appointed a dedicated Director responsible
for oversight and management of these
policies and procedures.
-
Evaluate performance and make principled
compensation decisions
-
Directors’ fee structure does not conflict
with
the
director’s
independence
or
discharge of his/her duties.
-
Measurable
performance
targets
for
executive officers (including the CEO)
to regularly assess and evaluate their
performance against set standards and
align compensation to performance.
-
Establish a Compensation Committee
comprising
of
independent
directors
to
develop
and
oversee
executive
compensation plans.
Effective Risk Management
-
The Board is responsible for strategically
establishing the company’s risk tolerance
mechanism, thereby developing a framework
and clear accountabilities for managing risk.
It reviews, by itself or by anointing external
independent parties, the adequacy of the
systems and controls in place to identify,
assess, mitigate, and monitor risks and the
sufficiency of its reporting.
-
Directors are responsible for understanding
the current and emerging short and long-
term risks the company faces and its
performance implications. Management’s
assumptions are often challenged, and
the adequacy of the company’s risk
management processes and procedures
are assessed.
1(GRI 102-18, 102-19, 102-32) | 2(GRI 102-5, 102-7, 102-10) | 3(GRI 102-26)


