Risk Management at Greenko is established on forward
planning, protecting autonomy, commitment to reach the
organization’s business objectives and the engagement of
senior management and the Board. Greenko’s risk profile
changes continuously and the risk management framework
effectively mitigates the potential impact to a level acceptable
to the Group’s strategy.
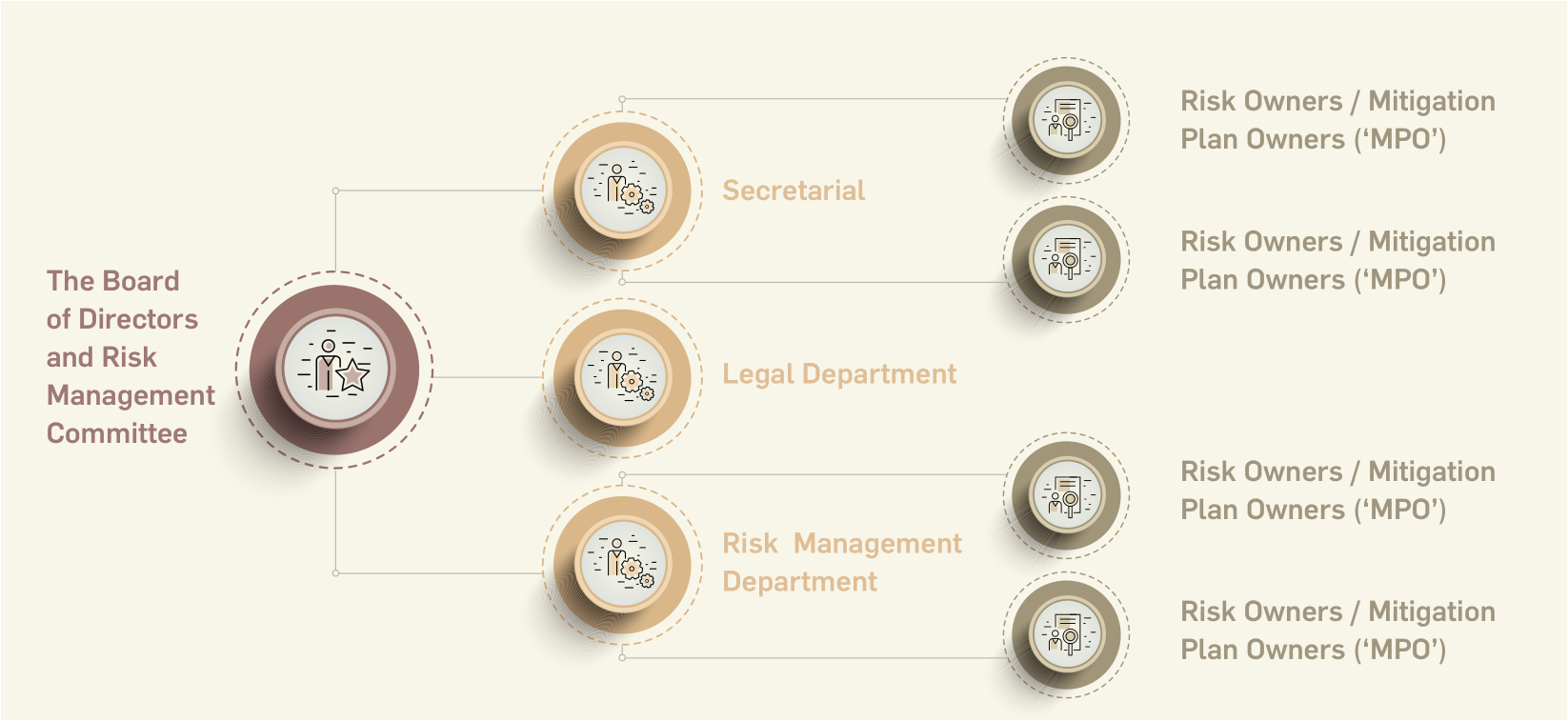
Risk Governance
The
growing
opportunities
in
renewable energy sector equally
possess certain strategic, functional
and operational risks. The elements
of risk management are judiciously
placed in Greenko’s organizational
structure and are well to harness
value pools. The board of directors and
the audit committee are supported by
the management to identify risks,
assess enterprise-wide effects, and
mitigate risks to create opportunities
out of it. An exclusive department
for risk management is created to
establish a framework and catalyze
the risk mitigation plan. Secretarial,
Legal and ESG departments assist
the Risk management department
in vesting the ownership of the Risk
Mitigation plan. This mechanism
has proved effective for Greenko in
driving risk management.

The integrity of our
business is continuously
tested in these uncertain
times. We, always ensure
that we conduct our
business responsibly
and ethically as this is a
part of our business DNA.
We perceive ethical and
professional behaviour
as our top priority and in
doing so we reinstate our
stakeholder’s trust.

- Vinay Bhatia
General Counsel
Risk Management Framework
The Greenko Risk Management Framework
(GRMF) is engineered to recognize and oversee
future risks and protecting the interests of
the organization’s business objectives. The
Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of
the Treadway Commission (COSO) and some
elements of Operationally Critical Threat,
Asset, and Vulnerability Evaluation (OCTAVE)
form the basis of GRMF. The internal risk
control systems are periodically monitored
by the Board and Audit Committee to identify,
manage, and address the risks.
GRMF allows the Board and management to
track and evaluate risks from an enterprise
standpoint, empowering the organization to
achieve the following business objectives:
-
Strategic- Aligned with VMV and Strategic
Objectives
-
Operations- Effective and efficient use of
resources.
-
Reporting-
Credible
and
reliable
disclosures.
-
Compliance- Comply with applicable
laws, regulations, codes, and voluntary
commitments.
Greenko’s top management plays a critical role in GRMF, while it is jointly handled by Risk, Legal and Compliance functions.
GRMF is used to evaluate risks related to any alternative ways considered by the management to meet the group’s strategic
objectives. In the instance of IRESP, prior to finalizing the size, scale, location, and timing, the management has determined
that their strategy is within their overall risk appetite. Greenko’s business-level objectives are achieved by focusing on business
strategy and objectives which are broken into sub-objectives for various activities such as GAM, Commercial, Projects,
Procurement and other functions.
Greenko’s Risk Management Framework
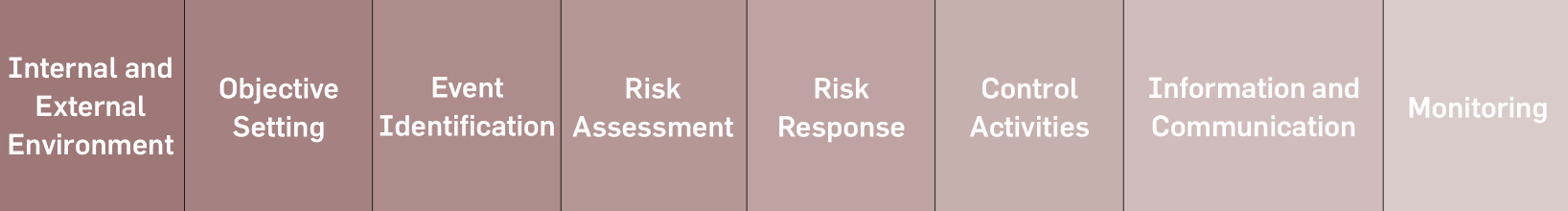
The Greenko Risk Management Framework consists of eight components2:
-
Internal
and
External
Environment
-
Examining
internal and external factors is
considered the most important
task. The Board sets a philosophy
regarding risk and establishes a
risk appetite.Further, it sets the
basis for how risk and control are
viewed and addressed.
-
Objective Setting - Objectives are
aligned to support the Greenko’s
Vision and Mission and are
consistent with its risk appetite.
-
Event Identification - Identifying
potential events from internal or
external environment affecting,
both positively and negatively, the
achievement of objectives.
-
Risk Assessment - Identified
risks, associated with hindrance
or enhancer of objectives, are
assessed
on
both
inherent
and residual basis, with the
assessment considering both risk
likelihood and impact.
-
Risk
Response
-
Possible
responses to risks, which include
avoiding,
accepting,
reducing,
and sharing risks. Management
selects a set of actions to
align risks with the entity’s risk
tolerances and risk appetite.
-
Control Activities - Policies and
procedures are established and
executed to help ensure the risk
responses.
-
Information and Communication
- Relevant information is identified,
captured,
and
communicated
in a form and timeframe that
enable people to carry out their
responsibilities.
-
Monitoring - Then the entirety
of
ERM
is
monitored,
and
modifications made, as necessary.
Risk Management Structure
Climate Risk Assessment and Management
Greenko is committed to ‘Climate
Risk Assessment and Management’
as part of its Risk Management
System, with the aim of making
informed choices, building capacity,
planning,
prioritizing,
mitigating,
and adapting measures to reduce
its vulnerability to climate change.
This entails proactive and systematic
identification and analysis of the
potential
climate-related
hazards
to Greenko’s operations, based on
projections of climate change models.
The integration of climate risk
assessment
in
the
existing
framework
was
carried
out
by identifying the physical and transition
risks of climate change that have
the potential to profoundly impact
Greenko’s business. Presently, the
climate risk assessment is conducted
for its critical operating sites.
Mitigating
climate
risk
is
a
continuous process and Greenko’s
Risk Assessment and Management
Framework enables the company
to build resilience against variations
in climate by taking account of all
the potential climate risks in its
operations and planning appropriate
mitigation strategies.
Scenario Planning – Risks and Opportunities
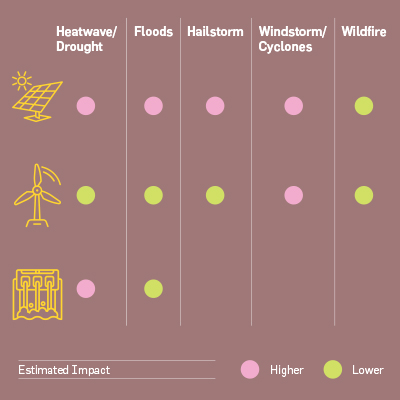
As part of its climate risk management
strategy, Greenko has over the short
term identified the risk of extreme
weather events and will implement
actions targeted towards reducing its
impacts on business. The company has
identified the above events using the
existing Early Warning System which
has now incorporated the monitoring
and warning of global warming induced
extreme events (acute risks), whose
frequency and severity are projected
to increase, owing to climate change.
This is crucial to proactively protect
and minimize the impacts of climate
change on the company’s assets and the
surrounding community, it operates in.
It is essential for the company to build
a resilient infrastructure and network to
mitigate climate related impacts.
Climate Risk Governance
The assessment of climate risk and
mitigation of its impacts is the first
priority for Greenko. To be able to do
this, climate risk assessment was
included in the GRMF as per suggestions
of the Board. Further, the company’s
Board of Directors reinforced Greenko’s
commitment to the UN’s Sustainable
Development Goals, especially numbers
7 — affordable and clean energy and
13 — climate action. The management
undertook the climate risk assessment
accordingly during 2020.
Climate Risk Strategy
While preparing a company’s future
strategy, the impacts of climate change
are
increasingly
taking
precedence.
Greenko has a vision of decarbonizing
the energy system through digitalization
and decentralization which has already
translated into strategic objectives and
the organization is pursuant to achieve
them. The group’s ability to capture and
convert
renewable
sources
into energy is always subjected to
material uncertainties of climate
change.
Greenko
continues
to
evaluate physical climate risk to its
own assets along with the electric
system in India to select a growth
strategy, choice of location and use of
technology.
Climate Risk Assessment
Greenko has examined the various
impacts
of
different
climate
scenarios in 2020, which included
the policy scenario of acceleration
of renewable energy adoption by the
Government of India and the physical
scenario of climate change as per
Global Climate Change scenario
RCP 4.5. This modelling confirmed
that the group’s business model can
tolerate the challenges that can arise
from climate change. The analysis
also put in place operational steps
at each site, in addition to the risk
assessment criteria, while evaluating
new assets and technology choices.
In the case of physical impacts
derived from the main climatic threats
and the increase in the frequency and
severity of extreme weather events,
Greenko has plans and systems to
improve the resilience of all assets
and components. Also, it has begun
discussions
with
the
insurance
institutions to cover climate risk
resulting in extreme weather events.
Greenko does not foresee that these
risks will have a catastrophic or
permanent impact on the assets
and
revenues.
The
organization
has a diversified portfolio of assets
spread across different states and
topographies.
Although
a
slight
increase in operational expenses is
anticipated, there are also plenty of
opportunities in the decarbonization
of the energy system in India.
Metrics and Targets
The climate change adaptation and
mitigation strategies are integrated
into Greenko’s Risk Management
Framework. A climate change specific
strategy has been devised and it
monitors and measures relevant
indicators such as its contribution
to the decarbonization of electricity,
under
GRMF.
Critical
business
indicators such as greenhouse gas
emissions, emission intensity across
the life cycle, water recharged and
reused, the extent of digitalization,
etc. assist the company to monitor
and plan targets.
The GRMF considers and monitors
the risks derived from climate
change:

1(GRI 102-11, 102-15, 102-33) | 2(GRI 102-34)