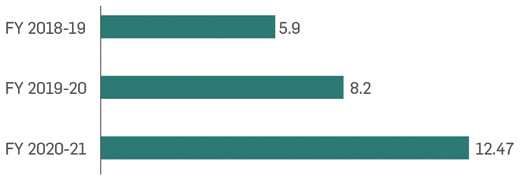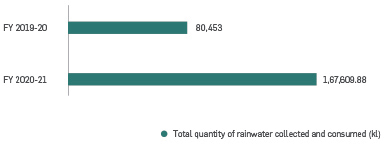Message from CSO
Dear Stakeholders,
This year has been disruptive and exciting.
Our robust business continuity systems
enabled us to continue our operations.
The pandemic, its consequent social and
economic disruption has offered unique
opportunity to the economy and society
to revisit the foundations. At Greenko,
we have harnessed this opportunity to
put together building blocks for the New
Energy Transition.

The ambition of Paris Climate Agreement
to limit the global warming to 1.5 degrees,
is driving governments, cities, businesses,
and entities at large to transition to a new
paradigm of energy, industrialization ,
production and consumption. Greenko’s
business model is designed to address this
challenge of deep decarbonization that
is inclusive, self-reliant, and ecologically
sustainable, in partnership with business
and government. Greenko’s three pillars of
Energy, Storage and Zero C Molecules’ Assets
support “Race to Zero” emissions and thus
avoiding cataclysmic social and economic
disruptions due to global warming beyond 1.5
degrees. Greenko’s solutions are curated for
transition away from fossil energy and carbon
chemistry with minimal reliance on carbon
capture and storage, thus ensuring just and
environmentally friendly transition. While the
business model and solutioning of Greenko
are aligned with sustainable development
pathway, we are sensitive to the need for
diligence and care during project planning,
execution and operations. Accordingly, we are
committed to Racing to Zero ourselves – ten
year’s earlier by 2040. We are signatories to
Climate Pledge and are working on a roadmap
along with our partners in the value chain
and co signatories of Race-to-Zero. In our operations gate-togate, the GHG footprint
is minimal, and we would ensure zero
emissions in the next few years. Our business
vision of Decarbonization, Digitalization and
Decentralization, requires us to grow our
energy, storage and Zero C Molecule assets
at a pace commensurate with our Net Zero
pathway. In this growth of assets, we will focus on low carbon input materials. While we
will be the catalysts in moving the ecosystem
along the value chain to decarbonization,
our ability to procure low carbon equipment
and machinery will depend on adoption of
decarbonization by countries, cities, and
 Greenko’s business
directly contributes to
UNSDG 13-Climate Action
and UNSDG 7-Affordable
and Clean Energy and
UNSDG 12-Responsible
Consumption and
Production goals.
Greenko’s business
directly contributes to
UNSDG 13-Climate Action
and UNSDG 7-Affordable
and Clean Energy and
UNSDG 12-Responsible
Consumption and
Production goals.

businesses. Besides, climate stewardship
along the supply chain, we will adopt circular
approaches in the management of our assets
- extend the life of assets, sharing models and
recycle, reuse, remanufacture during and at
the end-of-life of assets, to fulfil our climate
pledge.
As we transition and grow, we will continue
to adhere to our diligence practices
of Environmental and Social Impact
Assessments (ESIA) at the stage of design of
our projects and interventions, Environmental
and Social Management Systems in our
operations, embedded in Greenko Integrated
management Systems. Further, during the
reporting period, we have developed the ESG
framework delineating our ESG priorities,
our position on each ESG aspect and thereon
objective and targets. Salient aspect of
the ESG framework is increased role of
the governance in stewarding responsible
environmental and social practices. The
climate stewardship and circular economic
actions are the fulcrum of our Environmental
pillar. The Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
(DEI), Health and Safety, Retention and
Innovation and Customer Relationship will be
the foci of the Social pillar. The Governance
pillar will have focus on increased Board’s
role in stewarding ESG and Enterprise Risk
management including Cyber Security.
In our last and this Integrated Report,
we have outlined the results of physical
and transition risk on our operations
and mitigation measures that we have
undertaken. Going forward, climate risk
as also material environmental and social
risks will be a constituent of our Enterprise
Risk Management and will be periodically
reviewed by the Board. The ESG objectives
and targets will be dovetailed into KPIs and
remuneration/incentive mechanisms.
Greenko platform is agile and can resile to
be fit-for-purpose. In March 2020, when
the pandemic hit India. Greenko set up a
Covid Response Task Force and prepared a
multi-pronged action plan to respond quickly
to the evolving situation. Identifying the
requirement of oxygen and understanding
the evolving situation, the Covid Task Force
activated its global supply chain relationships
and focused on strengths to bring in critical
oxygen support infrastructure and equipment.
The focus was on expeditiously procuring the much-needed oxygen cylinders, oxygen
concentrators medical grade liquid oxygen
plants and cryogenic oxygen containers. The
company airlifted over 1200 medical grade
10 liters Per Minute Oxygen Concentrators
and created over 1200 oxygen beds in
remote locations and saved thousands of
lives. The concentrators were distributed to
rural hospitals in coordination with the state
governments. Today the revival of a defunct
60 TPD medical oxygen plant in Hyderabad
which would be producing over 45 tons of
medical oxygen has enhanced the overall
capacity of Telangana by 40%.
At the workplace, we implemented
disinfection and social distancing practices
and provided workers with personal protective
equipment. Employees leveraged technology
to minimize personal contact, even in dealing
with external stakeholders’ like vendors,
contractors, suppliers, regulators and
customers.
Greenko’s business directly contributes
to UNSDG 13-Climate Action and UNSDG
7-Affordable and Clean Energy and UNSDG
12-Responsible Consumption and Production
goals.
We recognize that the planet is at the brink,
and we must re-envision our relationship with
nature. We contribute to the conservation and
restoration of nature at our sites and across
the interconnected planet.
We continued our IR journey to be a more
equitable, inclusive, and transparent
company. Across the enterprise, we held
more than 4 formal IR conclaves, certified
around 250 Sustainability Practitioners. Going
forward, we see challenges in achieving our
own ambitious climate goals which include
decarbonizing supply chain and managing
assets post its life. Further, we must engage
and partner with governments, policy makers,
regulators, and businesses in managing
energy transition and “Racing-to -Zero” to
decarbonize both energy and industry. We
look forward to your continued engagement
to strengthen the endeavour towards green
and safe “Our Common Future”
Dr. Rambabu Paravastu
Chief Sustainability Officer
Strategic Approach
The business models of Greenko are closely integrated with value
generation from natural resources. Management of natural capital is always
embraced in Greenko’s decision-making process, risk mitigation plans,
strategic planning, and during the entire life cycle of Greenko’s projects
from design to operation and closure. The Group is in pursuit to extend
the life of the projects and assets by integrating such measures as a part
of asset management and also aspires to provide a second life for all its
assets to align with circular economy principles. Greenko is determined to
develop climate-resilient assets by periodically analysing the physical and
translational impacts of climate change on its project infrastructures.
The annual meetings at Greenko revolve around the discussions on shifting to a circular economy from take, make, waste models
and on circular resource management. Greenko has set up various short and long term goals to emphasize the actions to protect
and preserve natural resources. The environmental stewardship programs at Greenko are aimed at minimizing the operational
impacts, conceptualising business models in line with new climate normal and circular economy, protecting biodiversity, and
emphasizing digitalization across the operations as the first line of defense.
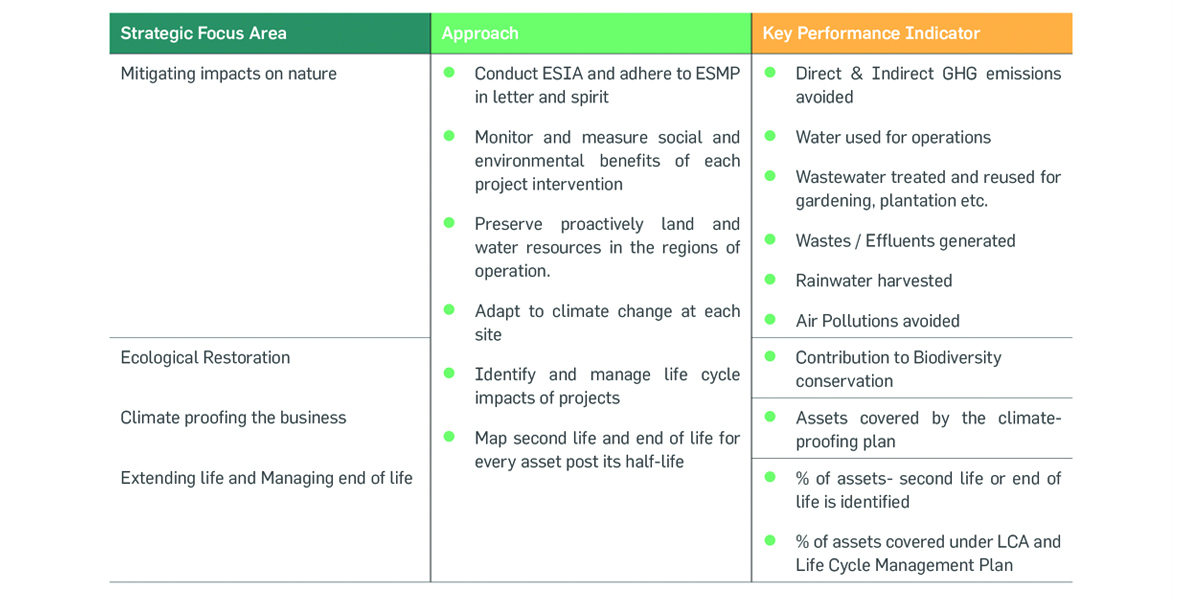

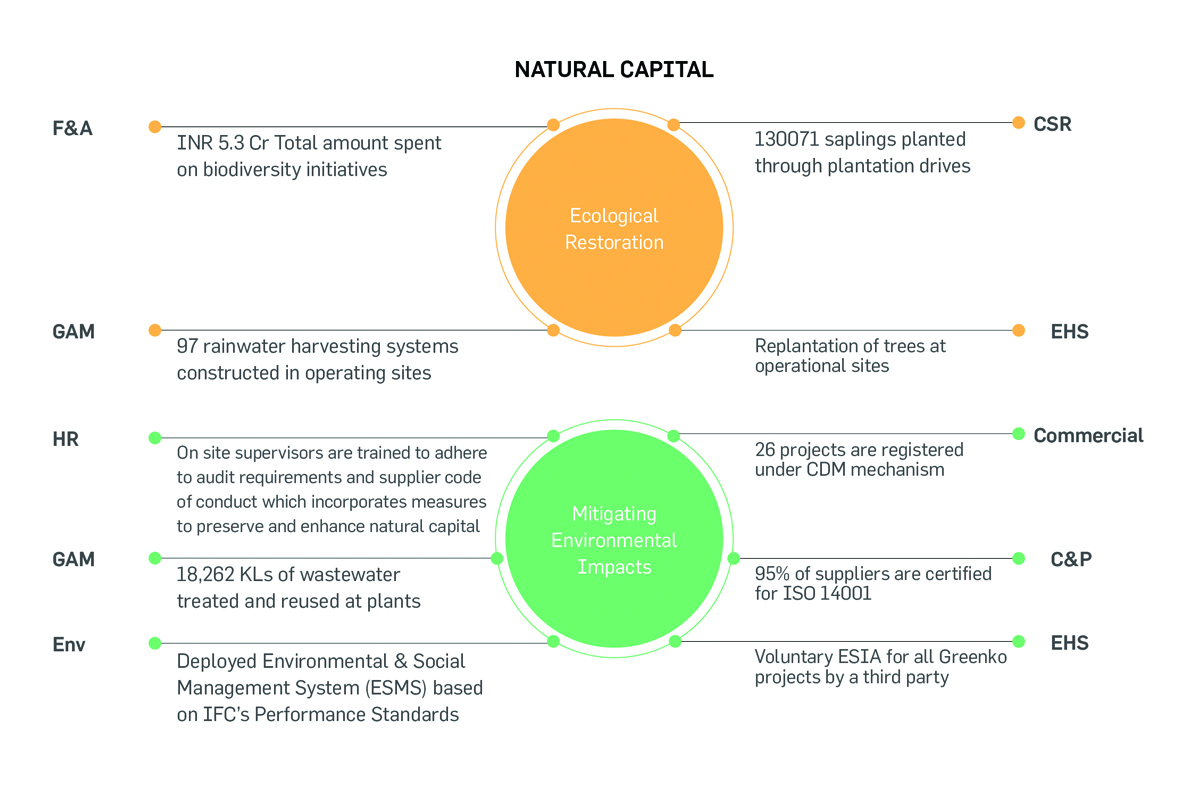
Integrated Value Creation in Natural Capital

Mitigating Impacts on Nature
Environmental Impacts & Mitigation Measures
Greenko endeavors to develop projects with minimum environmental impact
and thereby conducts preliminary assessment during the project planning
stage for promoting broader mitigation and conservation strategies. The
Group strives hard to understand the direct and indirect impacts of the
projects on the surrounding ecosystems and focuses to streamline its
operations efficiently to nullify the impacts to a great extent.
Greenko conducts Environmental and Social Impact Assessment (ESIA) study before project development, in line with the
requirements of ten Equator Principles; eight International Finance Corporation (IFC) Social & Environmental Sustainability
Performance Standards (PS); and IFC Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) Guidelines. This study helps the organization
proactively identify the adverse impacts of its operations on environmental resources. The impacts identified from ESIA study
are addressed through ESMP mitigation measures. Greenko adopts the following methodology for the implementation of ESMS.
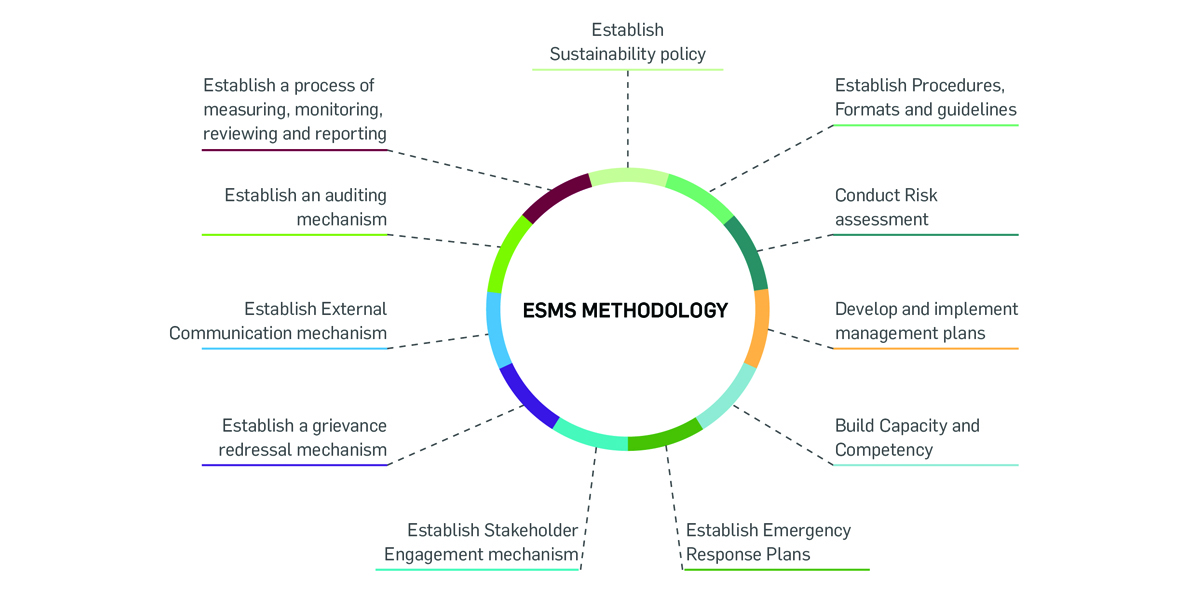
ESMS progress during 2020-21:
- Revised ESMS manual and ESMS procedures.
- Implementation of ESMS in progress at 86 sites.
- ESMS training provided to 160 participants covering 3 SBUs and 1280 hours of training hours.
Responsible Sourcing
Greenko Group is combining its efforts,
expertise, and experience in improving the
sustainability characteristics of its supply
chain through its Green procurement
initiatives. The Group makes efforts to
procure green alternatives from suppliers by
continuously holding engagements with them
and by incorporating Ethical, Environmental,
and Social principles and values in its
procurement strategies. This initiative helps
Greenko to evolve a broader perspective
and to establish long-term cost-saving
opportunities. The major activities discharged
as a part of Green Initiatives are as follows
- Creating awareness among vendors/
suppliers on environmentally preferred
goods and services
- Making at least 95% of critical suppliers
ISO 14001 certified and RoHS compliant
by March 2024
- Inclusion of environmental specifications
and evaluation criteria as per emerging
technologies in centrally managed
procurement
- Developing a collaborative approach
to optimize information-sharing,
consistency and performance
measurement, and Life-cycle analysis
During the reporting period, Greenko
has accomplished significant progress
in responsible procurement of standard
equipment and appliances. This initiative also
helped Greenko to adopt energy-efficient
fixtures and guidelines. Further to this, proper
planning for transporting raw materials by
consolidating packages from various vendors,
has significantly reduced scope 1&2 GHG
emissions up to 50%. The internal movement
of logistics from warehouses to flight
loading areas is monitored and optimized
to reduce GHG emissions. Greenko also
ensured that its major suppliers (95% in all)
are upgraded to ISO 14001 certification and
are RoHS compliant. Greenko also includes
Environmental criteria and specifications in its procurement policy and creates awareness
among its vendors on environmental traits of
preferred goods and services.
Green Alternatives Procurement
- Procured Energy Efficient Equipment
including Energy Star labeled electrical
appliances
- Encouraged energy efficiency retrofits to
move towards securing a BEE (Bureau of
Energy Efficiency, India) 5-star rating
Green Initiatives
Initiatives to improve the circularity of solar assets
- Greenko Group has initiated discussions
with manufacturers of PV Modules and
Inverters, regarding the inclusion of
circularity and life cycle approaches
throughout their value chain.
- Purchase offer evaluation included circular value assessment during (description & details)
- After assessing PV module manufactures,
Greenko has placed orders on the merit of
life cycle assessment and management.
Contribution to Climate Change Mitigation
Through delivering
renewable energy to the grid
and open access customers
, Greenko has avoided 12.47
million tons of CO2 emissions.
In addition, the group has,
till date, registered 26 Clean
Development Mechanism
(CDM) projects with UNFCCC.
Greenko addresses
the physical climate
change impacts on its
business performance
and sustainability. The
Group makes imperative
efforts to mitigate and
minimize climate change
risks on stakeholder lives
and ensures promotion of
sustainable well-being.
The impacts of extreme
weather events like floods
and cyclones on the critical
power infrastructures were
studied in detail, and plans
to build climate-resiliency in
the operations of assets are
being implemented.
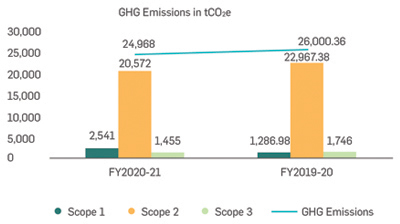
Direct and Indirect GHG Emissions
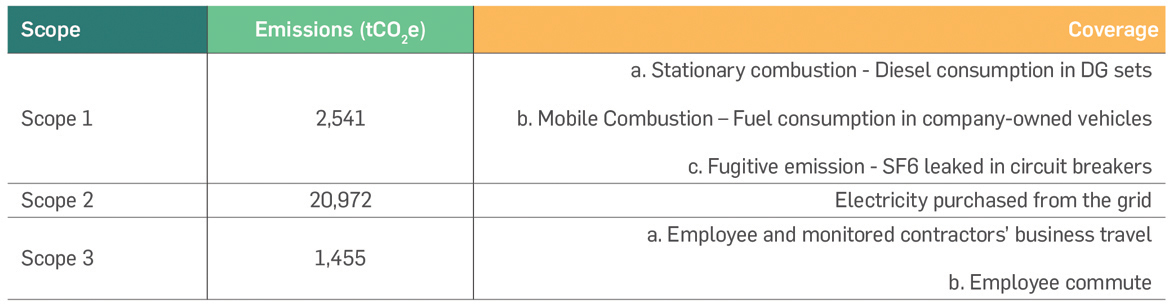
Scope wise GHG Emissions in last two financial years
The scope 3 emissions estimates are limited to only business travel and component. This obviously is a very small fraction of
scope 3 emissions. Greenko will assess and compute the scope 3 emissions covering all the 15 categories and report the same
in the next year report.
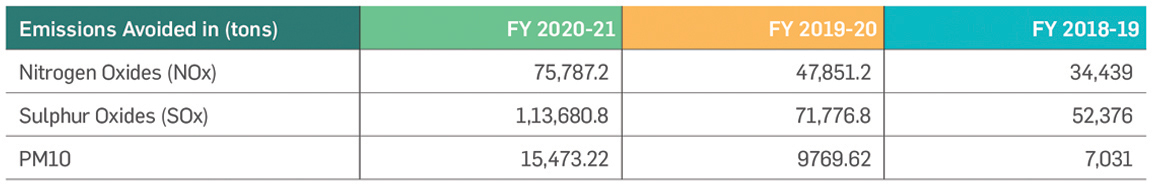
GHG emissions avoided
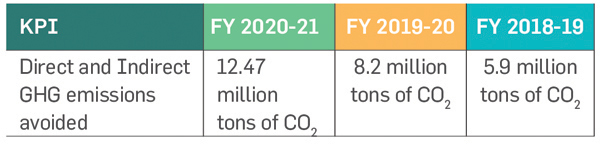
Direct and Indirect GHG Emissions avoided (in MtCO2)
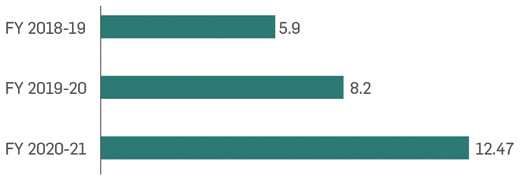
Emissions avoided
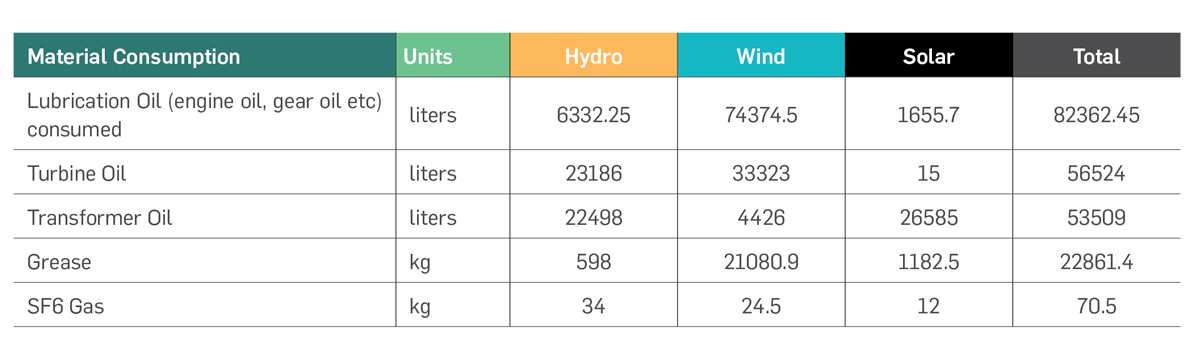
Material Consumption & Conservation
Wind, Solar, Hydro plants do not consume any input fuel for power generation. Thus, the fuel consumed in these plants are
primarily used for O&M purposes. The material consumption during the reporting year for the above is presented below
Greenko has instituted a Material conservation
program that aims to reduce the consumption
of raw materials, consumables, packaging
materials and also strives to increase the use
of recycled or bio-degradable materials. At
all the GAM plants, Greenko recycles scrap
refuse, consumables, and packing material as
a part of its material conservation program.
Following are some of the initiatives taken up:
- Short unproductive DC cables are
removed and reused in other areas
which resulted in an 8% reduction in the
requirement of new cables.
- Optimum use of Packing Material
by manufacturers/ suppliers, other
protection materials significantly
resulted in a 12% reduction in packing
material in the year 2020.
- At Zuvan Solar site the Electronic PCBs were repaired and reused for SPDs of SCBs and Inverter Cooling Fans.
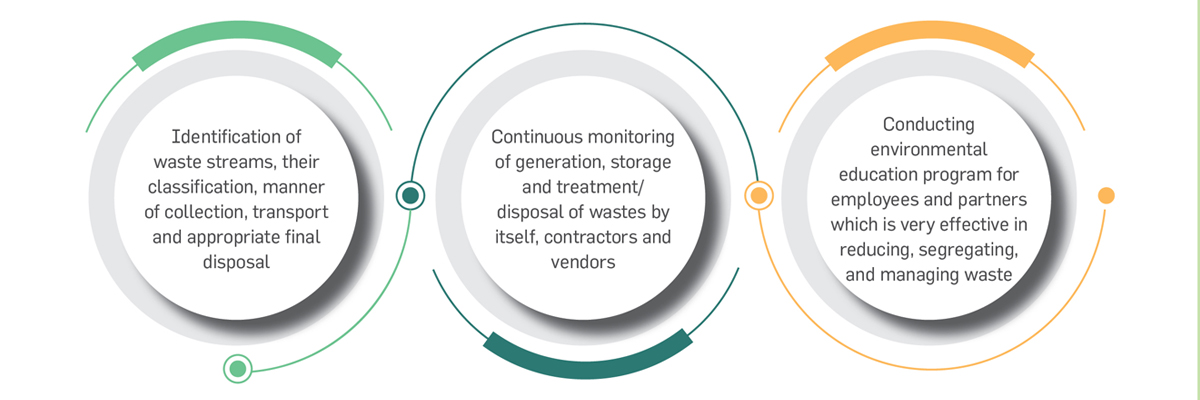
Waste Management
Greenko believes that circular economic practices will be the key element for driving sustainable development The Company’s
waste management practices adhere to the principles of Environmental and Social Management System which requires
conformance to legal requirements along with the reduction in waste generation through reuse or recycle, whenever possible.
The ESMS mandates to identify the waste streams within the organization and continuously monitors waste generation. Further,
ESMS also recommends creating awareness among key stakeholders to develop the circular economic culture. Greenko has
also initiated Plastic Protocol in this reporting year to delineate the usage of single-use plastics in operation and is exploring the
feasibility of replacing them with a sustainable alternative.
Waste Management practices at Greenko
Greenko conducts internal audits to quantify waste generation and to explore the potentials for incorporating the best waste
management practices. At operational sites of Greenko, this management program is carried out with the help of an authorized
third party, which involves monitoring garbage collection, segregation, and disposal of all the waste generated at the operating
premises. Segregated recyclable wastes are sold to authorized recyclers. A part of wastes requiring treatment before disposal
is sent to hazardous waste treatment facilities and others are used in landfills.

Waste Generation by type
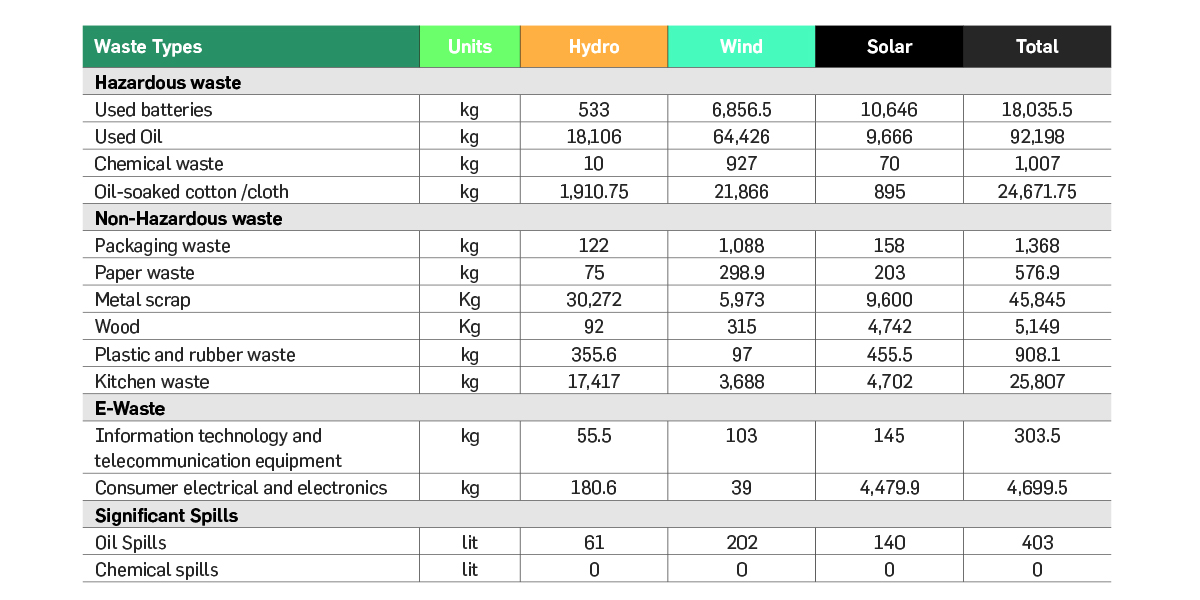
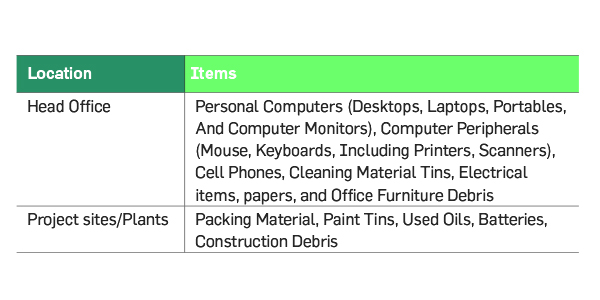
E-Waste Management
Greenko’s approach for waste management
includes Reduce-Reuse-Recycle-Reclaim-
Disposal to minimize its environmental
footprint. The Group stringently follows
E-Waste Management rules to treat and
reuse E-Waste resulting from technological
upgradations, capacity augmentation, and
other business processes. All these wastes
are collected by the ICT department which
is then segregated and recycled. All the nonreusable
hazardous e-waste, including lead
batteries, are disposed through authorised
recyclers approved by Central and State
Pollution Control Boards. In FY 2020-21,
the total E-Waste generated by operations
was estimated to be 4699.5 kgs. Greenko
also donates the unused computers and
other peripheral devices to various schools,
orphanages, NGOs, etc.
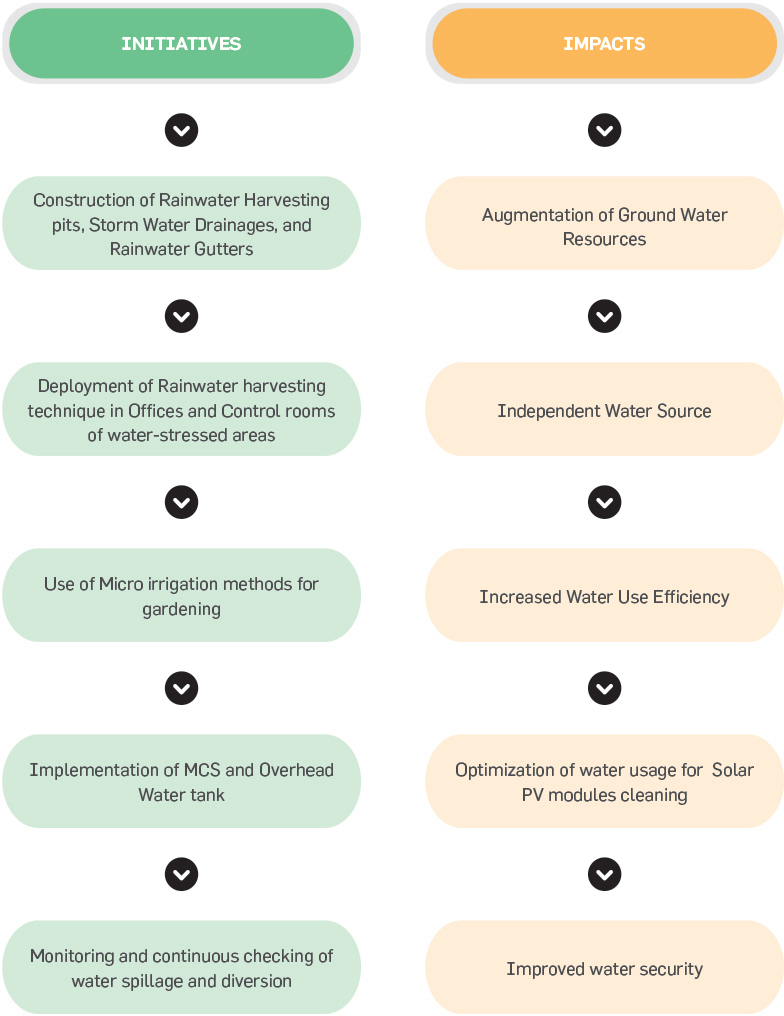
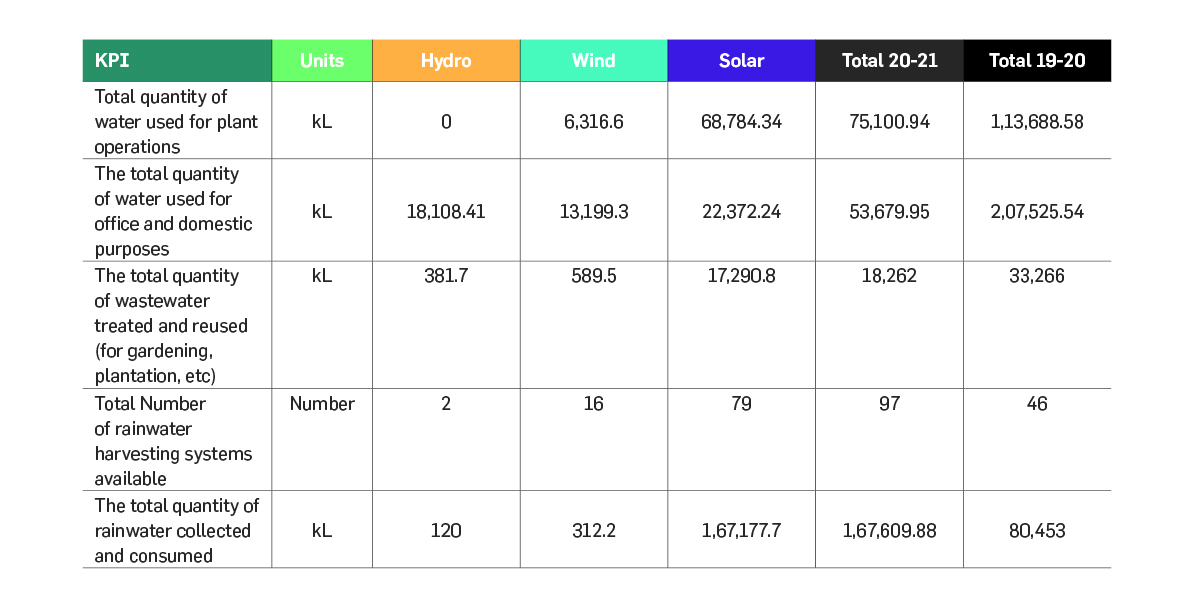
Water Management
Greenko’s operations are less water-intensive
and hence, water is mainly used for cleaning
of solar modules, domestic requirements,
construction, and biodiversity preservation
of the surrounding ecosystem. Greenko
continues to understand, monitor, and
record its freshwater usage, domestic water
consumption, operational water consumption
and wastewater discharge. Greenko closely
evaluates water use efficiency as one of the
criteria for exploring the feasibility of new
technologies and projects.

The impacts caused by its operations on
water bodies are carefully analysed by
Greenko and significant investments are
made to reinforce measures to limit such
effects. The main components of these initiatives are development of watersheds, rainwater harvesting, drip or
sprinkler irrigation and water-efficient cleaning technologies. The Group has
built various natural drainage structures, water recharge systems, and storage
facilities in and around its operational areas through which Greenko attempts
to harnesses rainfall. Through this, Greenko systematizes water requirements
of the surrounding community and operations. Through continuous efforts of
Greenko, the number of rainwater harvesting structures are nearly doubled and
the total quantity of rainwater harvested stands at 167609 kL.
Progressive in Water management practices at Greenko
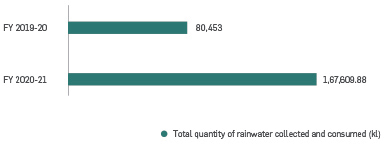
Water Management
Water Management Practices and its Impacts
Value Creation Story: Water Conservation at Zuvan Solar Plant
Location: Zuvan Solar plant
Summary
The main water sources of Zuvan plant are
a reservoir, bore well, and a pond. Reservoir
water is used for module cleaning and
conventional earth pit maintenance. Borewell
water is used for domestic consumption
and pond water is used for plantation,
gardening, and fire tenders. The plant is
reusing the module cleaning water for the
plantation of Aloe vera and Green grass
beneath the modules. This has also helped
in enhancing the module efficiency. Owing to
these conservation activities, the freshwater
consumption of plants reduced by 15% in the
current reporting year. In addition, various
pond restoration activities like dredging have
enhanced the rainwater potential of the pond.
The plant will continue its efforts and also set
a target for reducing freshwater consumption
further to 25% by the year 2022.
Key Achievements:
- Reduction in freshwater consumption by 15%
- An increase in rainwater storage potential of the pond
Energy Efficiency
Greenko is committed to adopting various
energy-efficient measures in its operations
to minimize the losses in generation,
transmission, and distribution and thereby
aspires to reduce its carbon footprint. Greenko
has implemented a multitude of energyefficient
measures in its operating locations,
some of which are enlisted below:
- Procurement of Energy Efficient Equipment in line with Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) Guidelines
- Replacement of conventional Lights with CFL & LED lights
- Regular maintenance of auxiliary equipment
- Operational management of hydro plants- arresting water leakage through proper grouting work in powerhouses
- Installing Light Arresters in between 33 kV line to reduce the breakdown time
- NRV Modification for pitch cylinder for reducing oil leakages in HUB (WTG)
- Installed Grease collectors which are used for waste or Excess grease collection from wind turbine blades to reduce breakdown time
- To capture real-time
data in-house application
has been developed by
Greenko. With the help
of this app ‘CELESTE’
Inverter operations
are being monitored
thereby improving power
generation
Ecological Restoration
Biodiversity
Greenko’s Projects are designed, developed, and operated based on extensive Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) carried
out during the planning stage. The company makes tremendous efforts to avoid setting up its operations in biological hotspots
and protected areas. Further Greenko proactively implements projects like habitat conservation, natural or sustainable farming,
protecting sea-based wildlife systems, fish seeding initiatives to restore, protect, and enhance biodiversity. Greenko has also
undertaken extensive plantation programs at all its operational sites to develop natural CO2 sinks.
Biodiversity Management
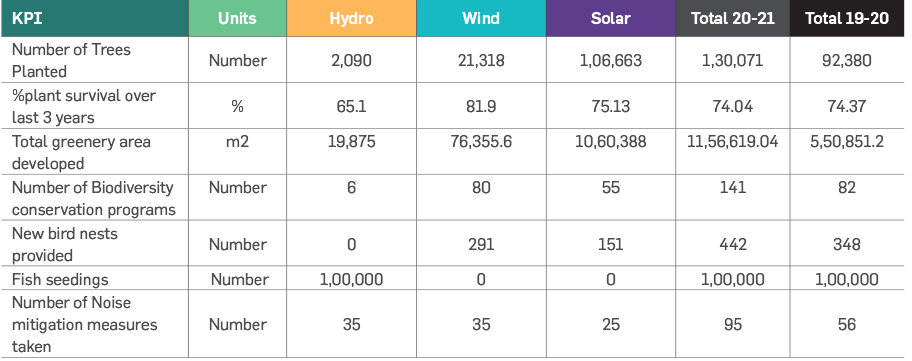
In addition, the Group is also supporting various Biodiversity Conservation activities and Natural resource management
programs in various geographical locations. To conserve and mitigate biodiversity loss, Greenko diligently conserves one
endangered species, each year, in the regions of its operations. During the last few years, the Group has contributed towards the
conservation of Olive Ridley Turtles, Great Indian Bustard & Red Panda.
Initiatives on Biodiversity Conservation and their Impacts


Climate Proofing the Business
Climate Risk Assessment and Management at Greenko
Greenko is aligning its business
models and asset management
practices to cope with the extreme
weather events resulting from
dynamic climate conditions.The
climate risk assessment is conducted
as a part of project management
to identify, analyze and mitigate
potential physical and transitional
climate risks. This analysis is
proactively and systematically
performed based on climate change
related events, trends, forecasts, and
projections.
Physical Risks
In this context, Greenko has assessed
the impact of physical risks across
different stages of its operating
lifecycle, such as,
- Physical impact on renewable resource potential
- Physical impact on generating assets
- Physical impact on Transmission and Distribution infrastructure
Transitional Risks
This category of risks mainly
corresponds to future policy changes
to aid renewable energy transition
Greenko has conducted climate
risk assessment for six of its critical
operating sites to assess and manage
climate risk vulnerability of assets
and their productivity. The six sites
are as follows,
- Ghani solar, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh
- SEI Adhavan, Tamil Nadu (Solar)
- Sneha Kinetic (Dikchu Hydropower project), Sikkim
- AMR Power, Karnataka (Hydro)
- Rayala Wind, Andhra Pradesh
- Tanot wind, Rajasthan
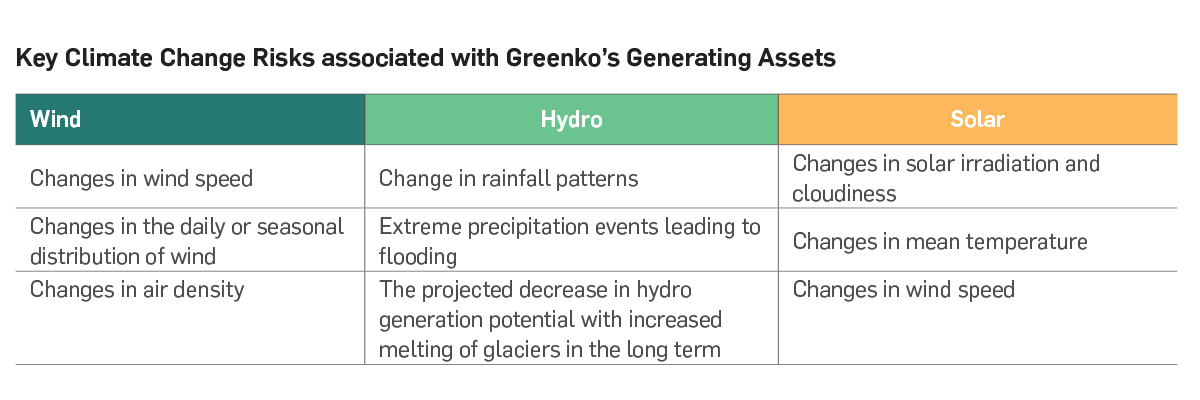
Greenko has studied and projected climate change impacts on its operations using IPCC’s RCP 4.5 scenario which
is the low-medium emission pathway (equivalent to 1.7-3.2°C temperature increase). The climate change projections
were studied for the period of 2020-2039 (Short term) and 2040- 2059 (Medium Term). The assessment revealed that
transitional risks are well-identified and addressed by Greenko. Physical risks like heat stress may possess certain threats
to operations and various water conservation and harvesting strategies are planned to mitigate those risks. The physical
impacts on resource availability viz., wind pattern, solar radiation, and hydrological flows are to be addressed through
agility, predictive and adaptive capabilities developed through Digitalization. The additional system and infrastructural
requirements to develop climate-resilient assets were also evaluated and planned accordingly.
Greenko Commits to Climate Pledge
The Climate Pledge co-founded by Amazon with Global Optimism in 2019
Net Zero Carbon by 2040
Part of UNFCCC “Race To Zero” and part of the solution - 10 years Early
- Community of
companies and
organizations,
working
together to
crack the
climate crisis
and solve the
challenges of
decarbonizing
our economy.
- Greenko Has
joined 114
businesses
across the
globe and
accepted the
challenge
of Climate
Pledge.
The Climate Pledge Requires the signatories to:
Extending Life and Managing End of Life
Lifecycle Management at Greenko
An LCA study is conducted for analyzing the
environmental impact of a product/system
across the various stages of its lifecycle. In this
case, the goal of the LCA study is to analyze
the environmental impacts associated with
the production of electricity from Greenko’s
different renewable energy technologies i.e.,
onshore wind plant (600MW), solar plant
(3000MW), and a pumped storage hydro plant
(1200MW) in line with ISO 14040 and 14044
standards and explore the feasibility and
consequences of the extension of life and end
of life management. A process-based LCA
approach was utilized for this study.
A cradle-grave LCA study was conducted i.e.,
the environmental impacts are calculated
over the entire lifecycle of the renewable
energy technology plants involving the
extraction of raw materials, manufacturing
of the components, assembling, transport,
operation, maintenance, and end-oflife
treatment. Through this study, it
was understood that the production and
disposal stages contribute to the maximum
environmental impacts of the onshore wind,
solar, and pumped storage hydro plants.
Although variables such as the production
of raw materials and components used in
the plants are not directly under Greenko’s
control, significant measures will be taken by
Greenko to ensure the proper recycling and
reuse of raw materials used in the various
components of renewable energy plants,
ensuring that the raw materials are not
ending up in landfills.
Environmental stewardship
Greenko adopts the concept of Environmental
stewardship which means ‘Being
responsible for all phases of the project
life cycle’. Through its strategic governance,
the Group has taken steps to minimize the environmental ramifications by committing
to various principles like Extended Producer
Responsibility (EPR), Design for Environment
(DfE), Reduce usage of toxic substances,
Impact assessment.
The Group carries out life cycle assessment
during the initial stages of every project
to minimize the environmental impacts
throughout the lifecycle of assets,
starting from design and development to
manufacturing, distribution, use, and disposal.
Greenko is also inspiring its suppliers to adopt
green practices thereby, culminating the
sustainability principles in its supply chain.
Life Cycle considerations are communicated
to the vendors through contractual obligations
and strict compliance is ensured. Several
Audit mechanisms are instituted by Greenko
to evaluate the environmental performance of Suppliers/vendors with
respect to Emissions,
Materials, Water, Chemicals,
etc.
Greenko is working with its
supply chain partners on
saving diesel by changing
the packing configuration,
changing the port etc. of
every order.
The Group also works for
a better End-of-life (EOL)
Management for the belowmentioned
products but, is
not limited to engaging the
certified Waste Carriers,
Hazardous Waste Disposal
License and Waste Operator
Licensees, etc.
Items covered under Environmental stewardship programs for EOL management
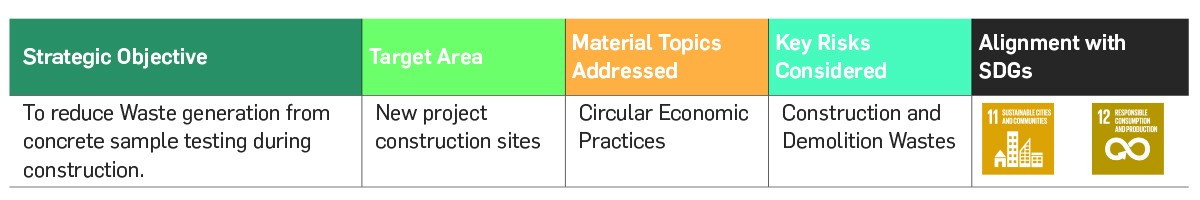
Value Creation Story: Recycle and Reuse of Crushed Concrete Cube wastes
Location: Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Telangana
Partners Involved: Jeori projects, Ghani Solar Project, Jilesh Power
Summary
Along with its partners, Greenko initiated
various projects to utilize the waste
concrete cubes generated from concrete
testing samples. The cubes are used as
alternatives for bricks in constructing various
structures like Walls, Pedestals, Steps, Water
tanks, Earth pit chambers, Poles. Greenko
will continue to give a second life to these
concrete cubes and continues to divert them
from landfills.
Benefits Achieved
- Diversion of Construction wastes from Landfills
- Reduction in Construction cost of new structures
Innovative Approach of the Project
Greenko has extended the life of concrete
cubes which would otherwise be sent to
landfills. These concrete cubes are stronger
than brick and hence, there is no additional
requirement for rendering works which result
in cost saving.
Value Created
The crushed cubes are used for construction of the following non-structural elements:
I. Construction of the following at plant areas and villages:
- Pedestal for containers and restroom walls, RO plants, etc.
- Construction of walls for water tank in the project area
- Kerb walls for roads
II. Base for cleaning area and ground clearance for storage material, drainage works.
III. Recycled aggregate/ crushed concrete cube used for pavement subgrade.
IV. To make cage wall for plants and trees

Construction of Surface Water Storage tank with concrete cubes, Madhya Pradesh
(GRI 306-2)
(GRI 305-1, 305-2, 305-3), (GRI 305-5)
(GRI 305-7), (GRI 301-1, 301-2)
(GRI 306-3), (GRI 306-4), (GRI 306-5)
(GRI 303-5)
(GRI 304-1, 304-2, 304-3, 304-4)
GRI (308-1, 308-2)


 Greenko’s business
directly contributes to
UNSDG 13-Climate Action
and UNSDG 7-Affordable
and Clean Energy and
UNSDG 12-Responsible
Consumption and
Production goals.
Greenko’s business
directly contributes to
UNSDG 13-Climate Action
and UNSDG 7-Affordable
and Clean Energy and
UNSDG 12-Responsible
Consumption and
Production goals.