Integrated Value Creation in Intellectual Capital
INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL
Journey so far
Energy system inherently is a complex and decentralization of the
energy generation systems to meet the needs of complex network of
demand points, comes with its own set of challenges. These include
ensuring quality of power, flexibility, reliability, and asset level visibility.
In addition to these issues related to cyber
security, integration of variable energy
resources among others. These can only be
overcome by rapid deployment of digitalization
and advanced innovative technologies. In
FY 2020-21, the need for digitalization and
innovation became evident with the Covid-19
pandemic. Greenko continued to invest in
technology and innovation with an eye for
future enabled technology that can fulfil the
necessities of an evolving energy market.
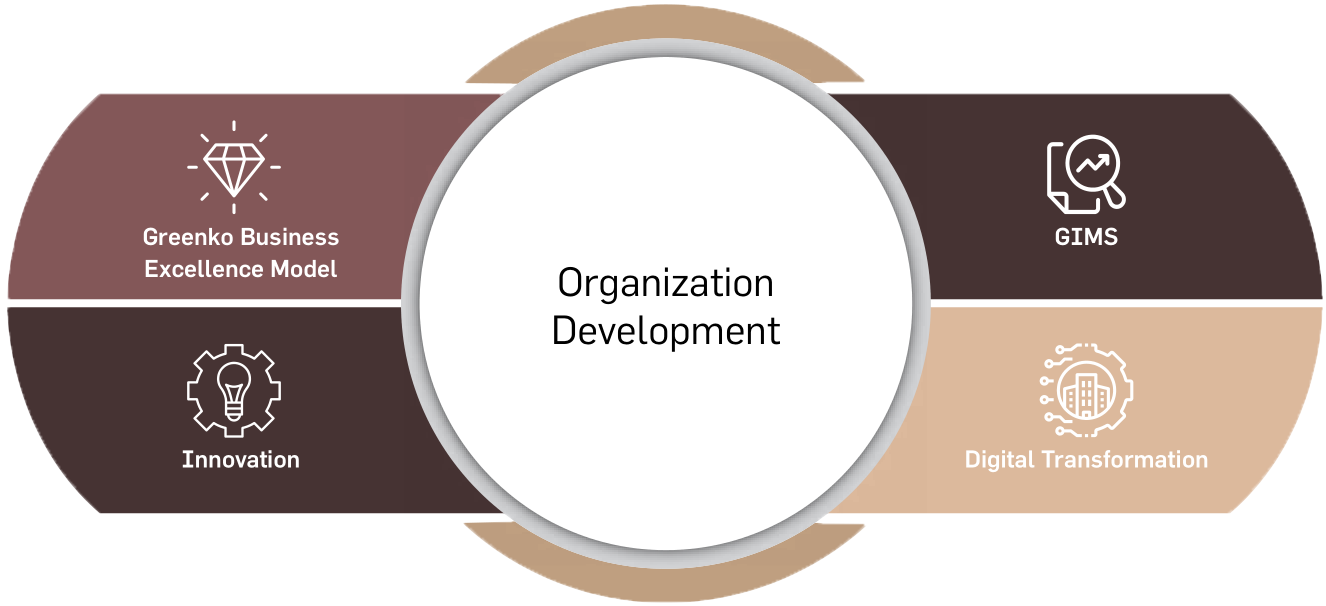
Greenko’s Organization Development Model
established in FY 2019-20 has carried on to
FY 2020-21 that governs intellectual capital,
to build capability and achieve excellence
by expanding, enhancing and fortifying
strategies, structures and processes.
The company believes in Business Excellence,
Digitalization,
Innovation
and
Systems
Assurance as components critical for its
transformational journey. The company’s
performance
of
intellectual
capitals
is
benchmarked,
monitored
and
improved
against these four decisive elements.
Greenko’s Organization Development Model
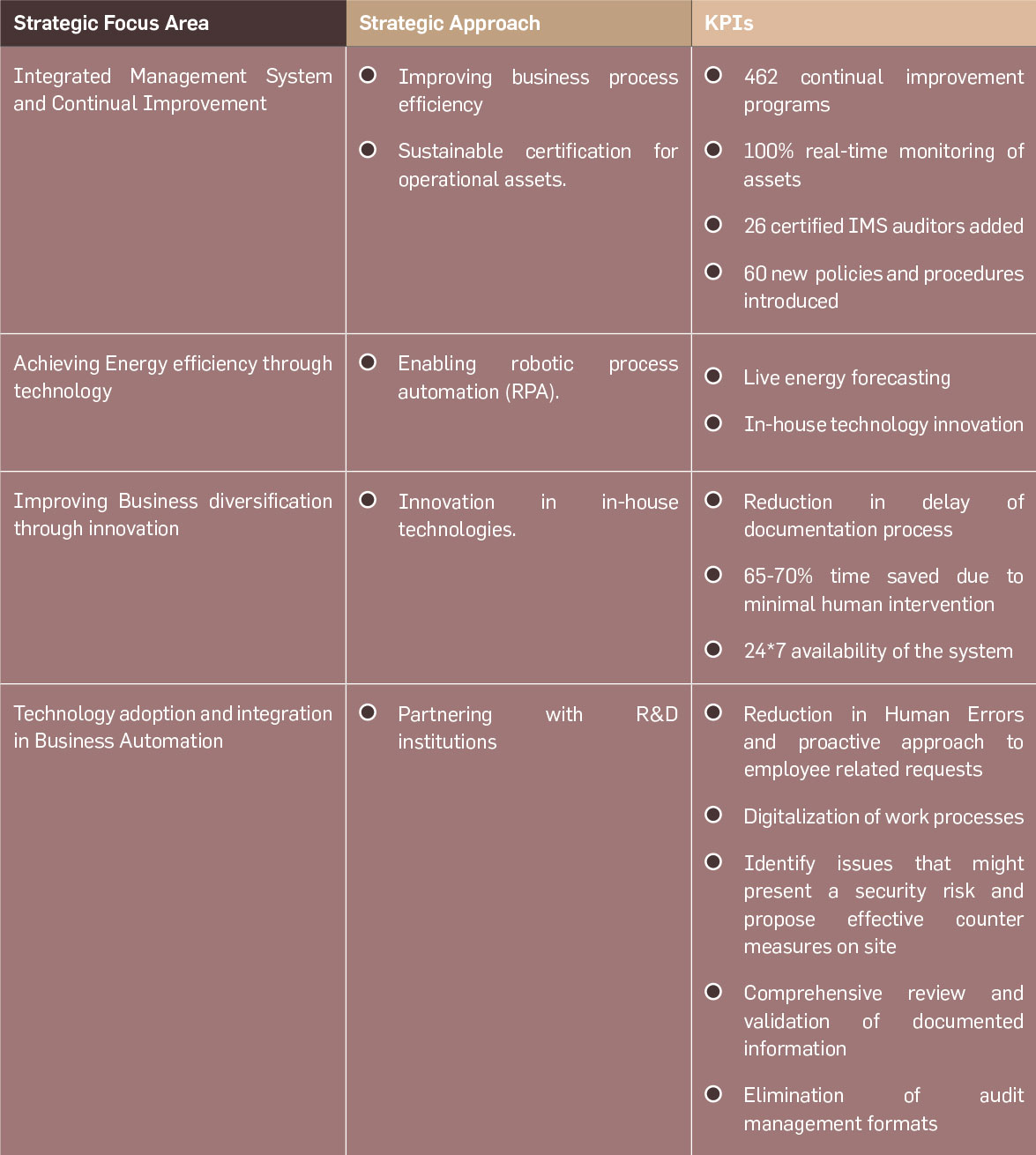
Integrated Management Systems and Continual Improvement

We have insulated our
business risks by ensuring
adherence to systems and
processes subjecting them
to non-financial audits. This
allows for empowerment
of our teams and promotes
innovation as the business
is in a constant state of
rapid evolution.
-Vidyacharan Astakala
AVP GIMS
Greenko’s Integrated Management System
(GIMS) is a continuous improvement and
performance excellence platform. The GIMS
amalgamates all the management systems
and processes across the group’s operations to
homogenize process management while also
sharing, monitoring and controlling systems.
Greenko Integrated Management System
(GIMS)
operates
in
accordance
with
international standards and industry best
practices to effectively align its numerous
management systems with the values, vision,
mission and strategy. Specifically, GIMS
works on the establishment, implementation,
integration, and maintenance of Quality,
Environment, Health & Safety, Information
Security, Energy and Social Accountability
Management
Systems
(QEHS-IS-En-SA)
as per the requirements of ISO 9001:2015,
ISO 14001:2015, ISO 45001:2018, ISO
27001:2013,
ISO
50001:2018
and
SA
8000:2014. In addition to ISO standards,
ESMS
(Environmental
and
Social
Management System) are maintained as
per the requirements of IFC performance
standards,
Sustainability
reporting
and
Integrated reporting is conducted as per the
requirements of GRI and IIRC Standards,
respectively and integrated into GIMS.

Greenko Integrated Management System Structure
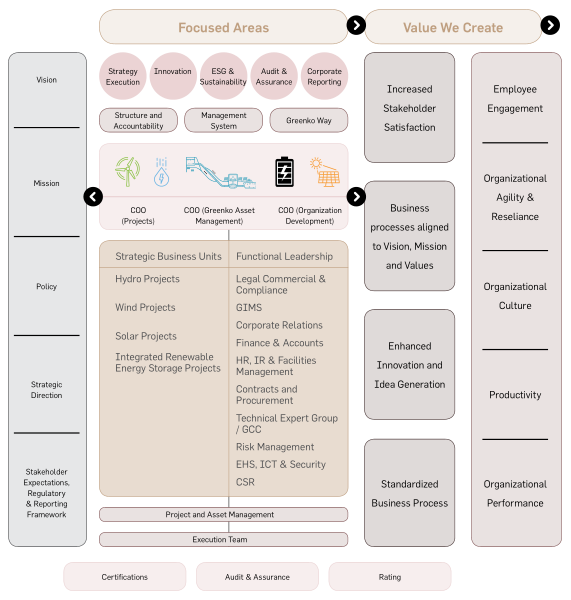
GIMS focused areas

The scope of GIMS includes training, implementation, auditing, certification and reporting as per ISO, IFC and IIRC frameworks.
The group has deployed diverse systems and associated processes across its operations for project management, asset
management, information management and sharing, forecasting and scheduling energy generation, real-time monitoring and
control of asset performance, surveillance, etc. All these systems and processes are integrated and managed under GIMS.
In order to achieve robust performance management and continual improvement, the deployed management systems and
processes are periodically and consistently audited to ensure adherence and effective outcome. The IMS audits are conducted
by both internal cross-functional teams and external agencies. The audit findings are promptly corrected.
In the current reporting period, EHS, GIMS, PPS (People, Process, System), OHS, GAM (Greenko Asset Management), and
ESMS (Environmental and Social Management System) audits were conducted across portfolios. Contributing to the continual
improvement, corrective actions were taken for the audit observations.
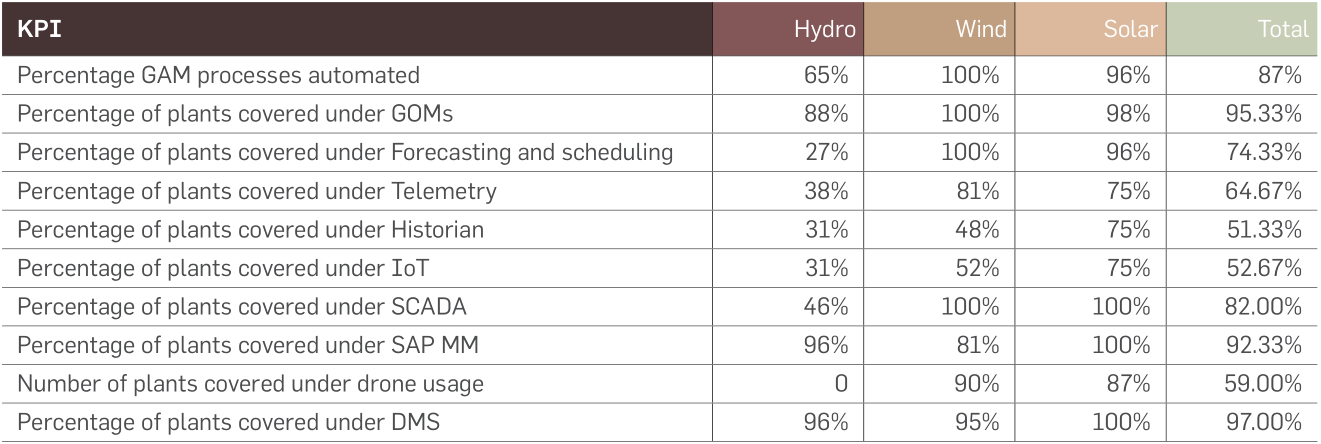
GIMS performance across BUs
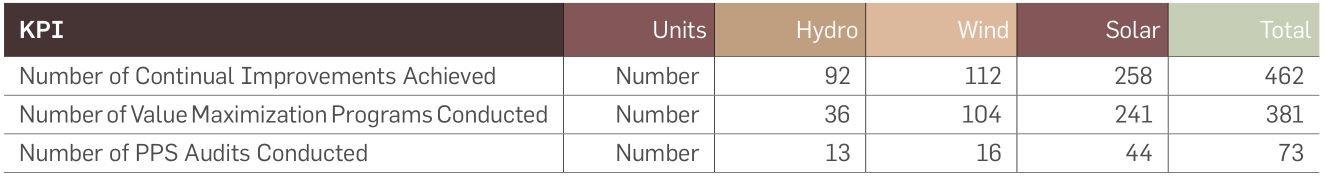
GIMS performance
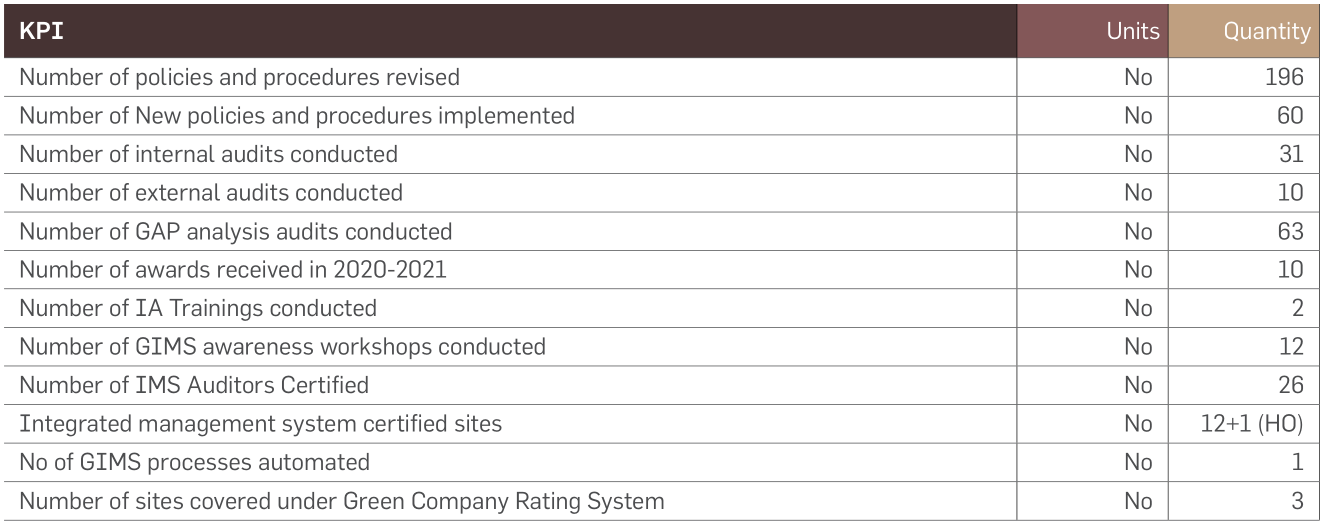
Value Creation Story:
Business Process Review and Updating of Documented Information
Location: HYDERABAD
Overview
To ensure a suitable, adequate and effective integrated management system across all Operational Plants, Projects and
Administrative Office functions GIMS has undertaken a project called “Business Process Review”. A committee was formed to
review and revise the existing procedures, identify and document new procedures. All the process documents were reviewed and
revised by the committee along with the process owners.
Following is the outcome of the Business Process review exercise:
-
Total Functional Areas covered under the exercise: 20
-
Total Procedure reviewed and updated: 208
-
Total Documents Controlled using Docu-sign: 208
Key Achievements
Adequacy and suitability of Documented Information
Challenges faced
Engaging relevant stakeholders on a single
platform for review of all Documented
Information
Achieving Energy Efficiency through Technology
Greenko believes in continuous improvement and innovation. Greenko
utilizes technology effectively to enhance energy efficiency there by
achieving the highest standards of operational performance.
Following are some of the technology laden initiatives designed to
cater to the needs of organization.
Value Creation Story:
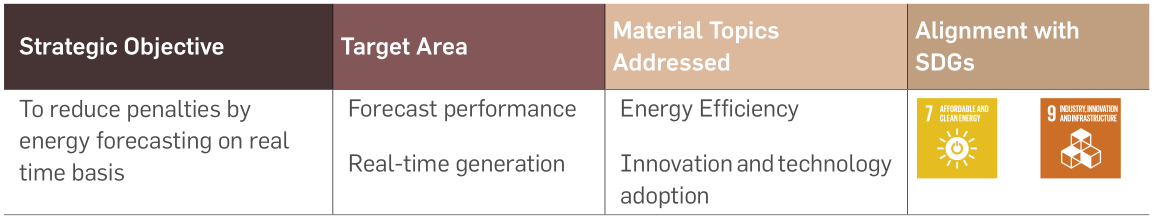
Energy Forecasting & Scheduling real-time analysis
Overview
As per the government initiative, all power plants in
the country must provide energy forecasting to the
Government agencies on day-ahead basis. In India,
it is especially important as the country is adding
hundreds of megawatts of variable renewable energy
generated from wind and solar power plants.
Energy forecasting needs to be provided on 15 Min
blocks starting from 00:00 Hrs. Block-wise deviation
(actual injected units to scheduled units) leads to
huge penalties. Greenko engaged multiple Forecasting
agencies along with its own forecasting team for
generation prediction.
It’s a painstaking task to understand/analyse whether
the forecasting agency is aligning with near real-
time generation. We have developed a dashboard to
present scheduled generation, real-time generation,
generation from other forecasters, penalties for each
time block for each plant, SBU wise & Group wise. This
software is extremely useful for the Greenko team
and the forecasters, eventually reducing penalties for
the company.
The tool also provides automated generation feeds to government agencies.
Value created
Greenko was successful in creating shared value by: -
Challenges faced
-
Coordinating with various forecasting agencies to automate the data feed to the software
-
Obtaining near real-time generation & availability data for all plants.
-
Structuring
data
for
different
government
agencies as per their own formats.
Value Creation Story:
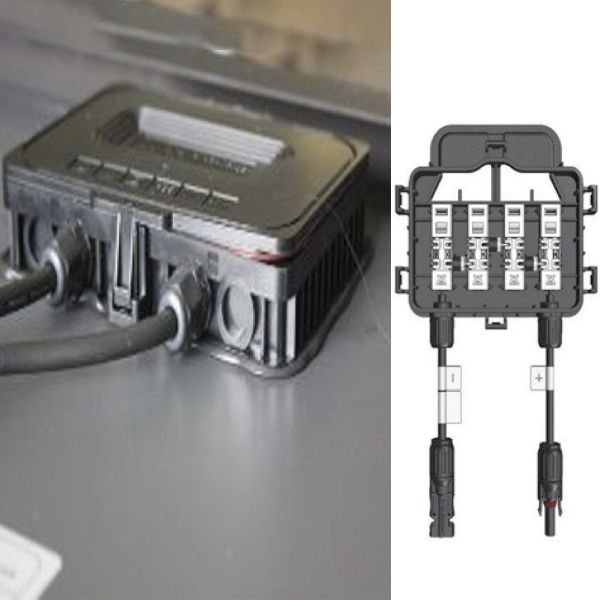
PV Module Junction Box Replacement
Overview
Junction box (JB) has a simple but important role in the working of PV modules. It is attached to the back of solar PV modules
with silicon adhesive and wired with 4 - connectors together and worked as the power output interface of the solar PV module.
Junction boxes have bypass diodes to keep power flow in one direction and prevent power from feeding back into the PV module.
It helps connect solar PV modules by cables with MC4/ MC5 connectors.
Greenko Innovation Hub
The company believes in and promotes
in-house innovation to address the unique
challenges of our business. To help facilitate
innovation within Greenko, a unique concept
of ‘Innovation Hub’ was initiated during FY
2020-21. It saw an overwhelming response
by all departments and participation from our
employees.
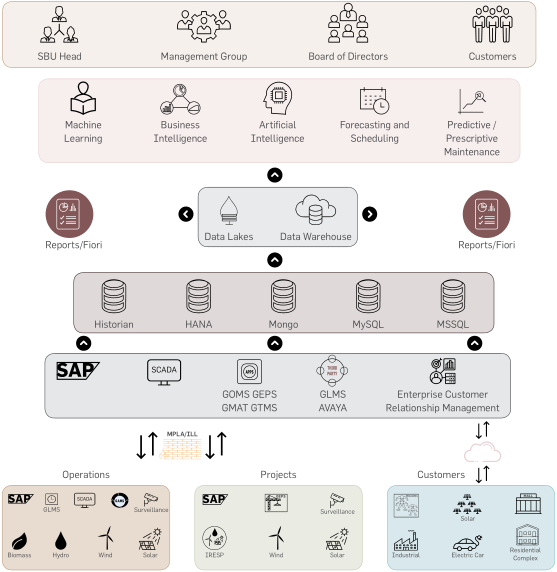
Technology adoption and Integration in Business Automation
Technology Adoption
Greenko group has been at the forefront of adopting technology to transform energy systems. Digitalization of
energy systems has enabled predictability, reliability and sustainability. Vision to sustain dynamic growth by utilizing
technology to improve business operations.
The digital transformation roadmap created the year before has yearned good results. Greenko adopted smart data
analytics, forecasting and scheduling of energy models, cloud computing, IoT based SCADA systems, monitoring of
assets by drones, recording with historians etc. The use of advanced technologies has provided valuable foresight in
operations and reduced downtimes and increased the reliability of remote assets.
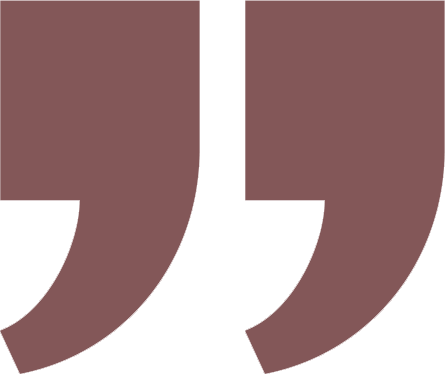
Greenko’s Digitalization Journey
ICT Model
Functions of ICT
Value Creation Story:
Darwin Box HRMS implementation
Location: Across the group
Overview
Greenko took the initiative of implementing Darwin Box HRMS. It carried out Employee lifecycle management through various
modules. The implementation was as critical as choosing the right HRMS.

Value created
Greenko was successful in creating shared value by: -
Challenges faced
The
challenges
faced
during
the
implementation were:
Value Creation Story:
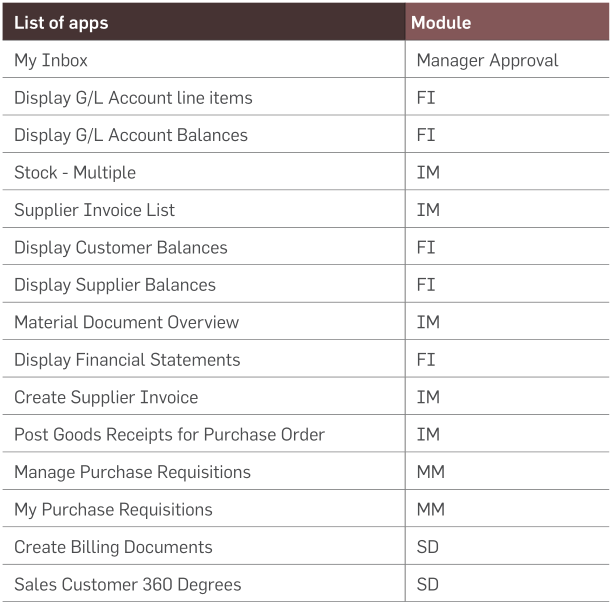
Fiori Apps Implementation
Overview
Before Implementation of these apps, users accessed the system for any activity within the Greenko network through SAP
Classic GUI and required VPN access for SAP access from outside the network. New S/4 Hana Interface has been implemented
to enhance user experience and performance.

Innovative approach of the project
After Implementation of apps, users can
access the system through the web with
multiple devices like computers, tablets and
mobiles. Users outside our network can also
access services through secured web access,
which improves mobility, scalability, and
productivity.
The apps are light and web based and are
easily accessible with minimum bandwidth,
from remote areas . Earlier, SAP GUI was
required and bandwidth requirements were
also higher.
Users can easily access role-based activity
from Fiori Apps tiles. Earlier, a user had to
remember the transaction code for calling
the transaction and performing the desired
activity.
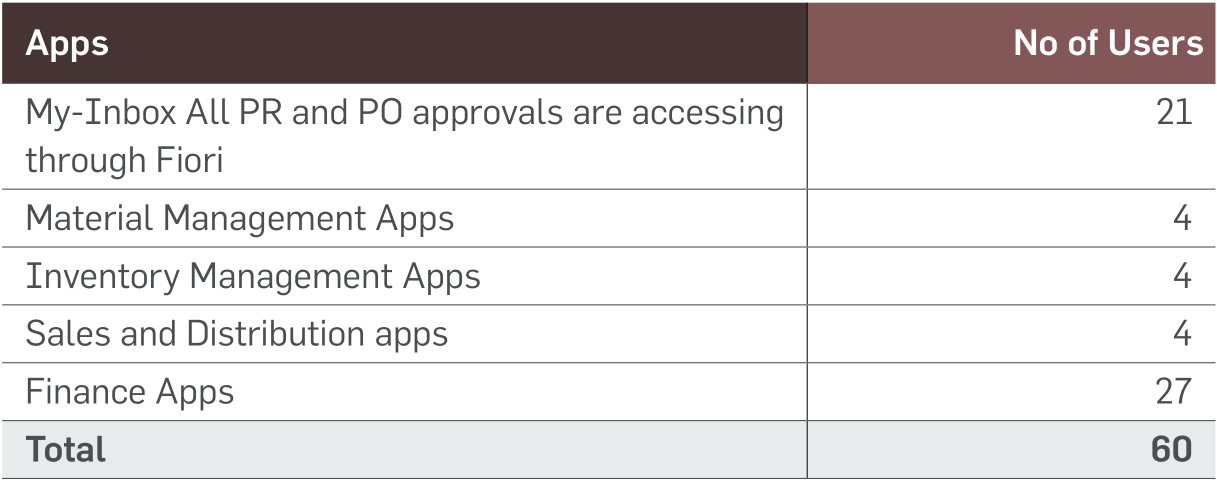
List of Fiori apps which are implemented
Challenges faced
-
Identification
of
suitable
apps
commensurate
with
user
needs
and tailoring functionalities as per
expectation.
-
User adoption is difficult for Business
users who have to migrate to GUI to
Apps Training on Fiori Apps.
Value created
Greenko was successful in creating shared value through the following steps: -
-
Harmonized design, structure, content to
provide simplified user experience on the
digital platform
-
A role-based user experience provided
end users access to information and
functions needed for daily work
-
Users could Transfer/delegate approval of work-items to other users
-
All kind of approval PR or PO floated
into a single workspace - My Inbox app,
aiding managers to take decisions.
-
Finance Reports like finance statement,
GL balance and details, Customer and
supplier balances were enabled
-
MM users viewed purchase requisitions
and managers could assign it to buyers
-
Inventory users could view available
stock, supplier invoice lists and could
perform functions such as receipt issue
and invoice posting.
-
Enabled monitoring of customer orders, information and bill generation
Key Achievements
-
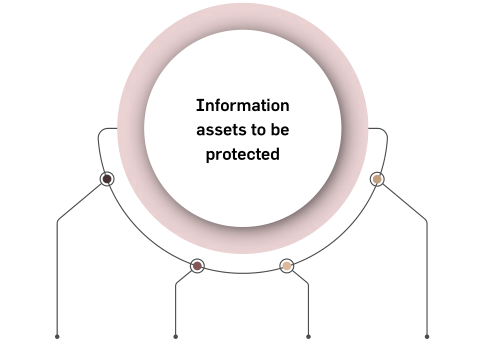
Secures information with Four Layers of Information Security
An ISMS helps protect all forms of
information, including digital, paper-based,
intellectual property, company secrets, data
on devices and in the Cloud, hard copies and
personal information.
The four layers represent the way information
flows within and between systems. Securing
each of the four layers include: Perimeter
Defense, Host Protection, Operating Systems
and
Application
Protection,
and
Data/
information Protection. One method to secure
the four layers is encryption.
-
Helps respond to evolving security threats
Constantly adapting to changes both in the
environment and inside the organization,
an ISMS reduces the threat of continually
evolving risks.
-
Protects confidentiality, availability and integrity of data
Through a set of policies, procedures,
technical and physical controls to protect
the confidentiality, availability and integrity of
information.
-
Improves company culture
Its holistic approach covers the whole
organization, not just IT,
and encompasses people,
processes and technology.
This enables employees to
readily understand risks and
embrace security controls
as part of their everyday
working practices.
-
Offers
organization-
wide protection
It
protects
your
the
organization
from
technology-based risks and
other threats such as poorly
informed staff or ineffective
procedures.
-
Reduces
costs
associated
with
information security
The risk assessment and analysis approach of
an ISMS enables the organization to reduce
costs spent on indiscriminately adding layers
of defensive technology that might not work.
-
Increases resilience to cyber attacks
Implementing and maintaining an ISMS
will significantly increase the organization’s
resilience to cyber-attacks.
-
Information Security Governance
The advancement of IoT/IIoT has created
new value through the interconnection of all
manner of ‘things’. However, cyberattacks
are growing more sophisticated every day
and their range of targets have expanded
from traditional ICT to the Internet of Things
(IoT) and to OT which encompasses control
and operational technology. To minimize risks
such as information leakage and business
shutdowns that impact the continuation
of business itself, risk management as it
pertains to information security is one of the
most important issues a business faces.
At Greenko, we follow the characteristics
of effective security governance which are
critical for an effective enterprise information
security management system.
- Considering
information
security
management as an institution-wide issue
- Making leaders accountable.
- It
is
viewed
as
an
institutional
requirement (cost of doing business)
- It is risk-based.
- Roles, responsibilities and segregation of duties are defined.
- It is addressed and enforced in policy.
- Adequate resources are committed.
- Provision for staff training.
- Requirement of a development life cycle.
- Planned,
managed
and
measurable
outcomes.
- Reviewed and audited.
-
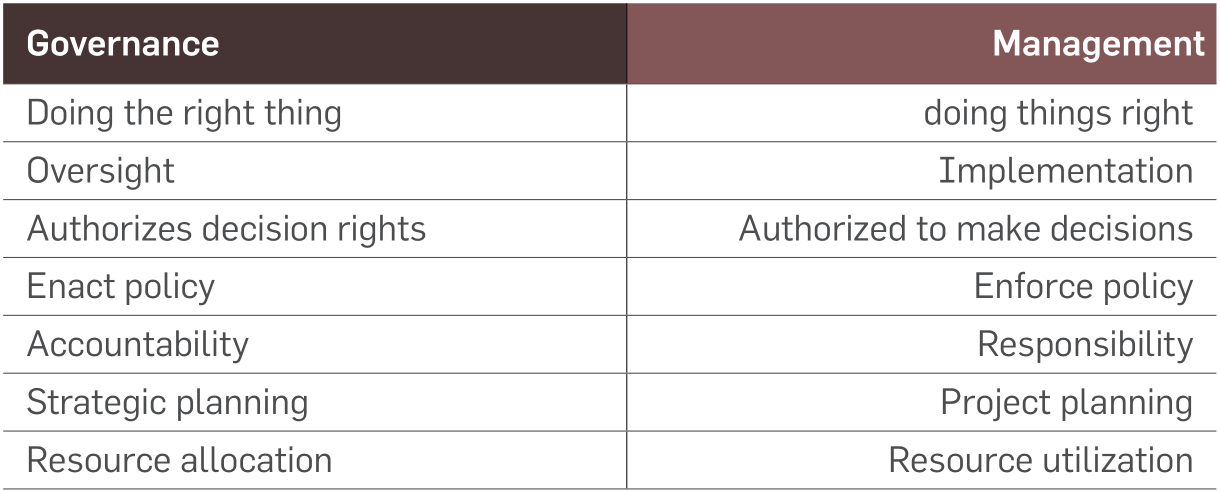
Information Security Management
Often
Information
security
governance
is
confused
with
Information
security
management.
Information
security
governance is the system with which an
organization directs and controls Information
security. Information security management
is concerned with making decisions to
mitigate
risks;
governance
determines
who is authorized to make decisions.
Educating employees on information security
An organization's ability to maintain information security and protect personal and confidential information depends on its
workers understanding of the importance of information security and making it a part of their personal ethos as they go about
their daily tasks.
Greenko conducts security awareness sessions annually on information security for all executives, workers, and temporary employees.

On-site security risk assessment
With an ever-expanding pan India presence,
the Greenko Group is present in many states
and has power plants among its business
entities. This environment inevitably gives rise
to diverse in-Group network environments
and facilities and varied installation and
usage environments for IT equipment. There
is also communication with outside parties
via internet connections, removable media
(USB storage) and other means. Preparing
for security risks such as spear phishing and
malware infection is very important.
To address the risk that comes with changes
to the business environment, Greenko has
strengthened its assessment framework
that uses expert security teams. Specifically,
a security team will coordinate with each
power
plant
SCADA/ICT
person
and
implement enhancements from the following
perspectives:
- Carry out assessments of all assets and
internal facilities that connect to the
network of the Greenko Group based on
latest developments.
- Identify issues that might present a
security risk and propose effective
countermeasures on site.
Challenges Faced
- To make everyone understand that
ISMS is not an ICT Team responsibility,
rather everyone’s responsibility at the
organization.
- Incorporating ISMS in their existing procedures for non-IT functions.
- Understand asset-based risk mitigation.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (IoT)
Over the years, Greenko has transitioned towards a more technology enabled company and has been at the forefront to implement
Internet of Things (IoT). This has allowed Greenko group to function with utmost ease during a difficult year that included the
pandemic. The group’s solid digital infrastructure along with possibilities in IoT and Big-Data Analytics have allowed for remote
access of data to optimize business operations.
Integrating Technology in Business Automation
Utilizing the right kind of technology is crucial for the company’s growth. Greenko has become technologically efficient by
using SAP processes, robotic process automation (RPA), business process automation (BPA) and AI-powered automation.
These processes are tailored specifically to the needs of the organization and have helped a lot in automating routine tasks and
significantly reduced manual intervention during Covid-19, reducing overall operational costs. Allowing automation in business
processes enabled Greenko to continue operations with minimum complications during FY 2020-21, while enabling us to work
remotely.

SAP Integration and Management at Greenko
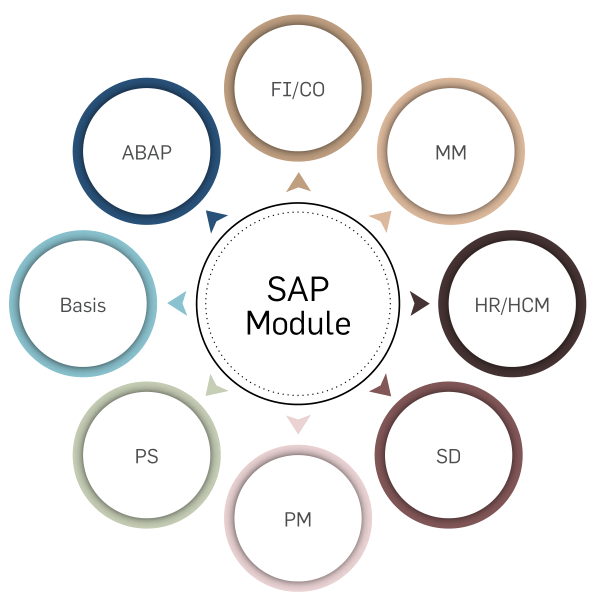

Strategic partnerships provide
access to industry experts that
we can work with and build
on each other’s strengths to
enhance our security. Prudent
collaborations have given us a
better cybersecurity posture
for our operations against
the ever-increasing threat
landscape.
-Thirumala Raju Mandapati,
AVP ICT
Digitalization of BUs
Value Creation Story:
AI – Robotic Process Automation
Overview
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) process has been implemented for automating the process of MDM: Master data management
(i.e Material, Vendor creation & extension) in SAP and Forecasting data.
MDM process:
Helpdesk tickets are received for material creation or extension from all user departments like Stores and O&M Team. Tickets
are received from both Finance and C&P Team for Vendor creation.
By implementing RPA, we use the software BOT for repetitive works. Users fill predefined templates and BOTs read the data to
initiate the creation or extension process after validation.
Forecasting data process:
Forecasting Team has to feed the forecasting data for each state into the portal and email the same to concerned people at
regular intervals. Previously, teams performed this task 24/7. After implementing the RPA, the processes were automated for 3
states including Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh.

Innovative approach of the project
Key Achievements
-
Better accuracy
Robots do not make mistakes. They are compliant and consistent.
-
Increased speed and productivity
BOTs perform the activity three times faster than humans and automates processes.
-
Scalable
RPA performs a wide range of operations at the same time.
Value Created
Cost savings
For master data management an average of 2 people were
require for material/vendor creation and another 2 people were
required for validation. After BOT implementation, the manhours
for master data creation has been reduced significantly and the
resources were optimally utilized in other areas.
By automating the forecast process, we have reduced 6
resources for 3 states and we can utilize resources in other
productive areas.
Value Creation Story:
Path of Digitization and Decentralization
Overview
Main purpose of digitalization is to obtain real time data,
decentralize decision making and eliminate paper consumption
to reduce burden on the environment. It enables automation,
enhances data quality, collects and structures data to aid
easy and quick decision making. Manual process involves a
lot of paper consumption. It takes more time to complete a
form due to absence of concerned people and it is difficult to
analyse the data. We faced many problems with the manual
process and it delayed documentation
Innovative Approach of implementation
Quality issues and details of a project can be accessed at one
single place and in real time. It is easy for senior management
and business heads to review project progress from anywhere
and in real time. Graphical dashboards provide ‘Quick
Visualization’ of project progress and project QA clearances in
real time. Rather than manually checking lists, QA clearance
for project stage is carried out online.
Value Created
Presently, the company has digitized the Quality deviation
management process at Greenko Energy Projects System
(GEPS). We are working with online QA process through
the Greenko Quality Assurance Portal (GQAP) which will be
implemented for future projects. Digitization has helped us to
save paper and run eco-friendly operations
Value Creation Story:
RPA implementation in Greenko
Overview
Greenko is increasingly turning to automation to improve
process efficiency, employee productivity and cut redundancy
and costs. Adopting automation has enabled streamlining of
operations and the deployment of robotic automation tools.
Identified Processes which are automated:
- Vendor and Material Master Management
- Forecasting data update

Innovative Approach
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a program that follows
rules and instructions to imitate human actions on applications
that involve repetitive tasks. With user-friendly features, it
helps to streamline processes easily. It performs common
tasks such as queries, cut/paste, merging, button clicks, etc.
Key objectives of implementing Robotic Process Automation are as follows
- Improve customer satisfaction
- Improve accuracy
- Manage controls
- Increase efficiency
- Reduce monotonous work
- Save cost
- Skill upgradation of personnel
The Center of Competence and innovation was created
at Greenko Group in October 2009. It deployed the first
software Robot (SAP Master data Automation) at Greenko. The Worldwide practice of using business Robotics, using RPA, demonstrates higher efficiency of the tool in achieving the objectives
of business transformation, which is the basis of the concept of strategic development of Greenko.
To further develop and apply RPA at Greenko Group, the project on the diagnosis of business process was implemented and
conducted along with external consultants. As a result, the processes suitable for automation were identified, recommendations
for the modernization and expansion of the Center of Competence were received. Software robots were developed independently
by the RPA Center of Competence at Greenko Group
High-level view of Robotic processes automation
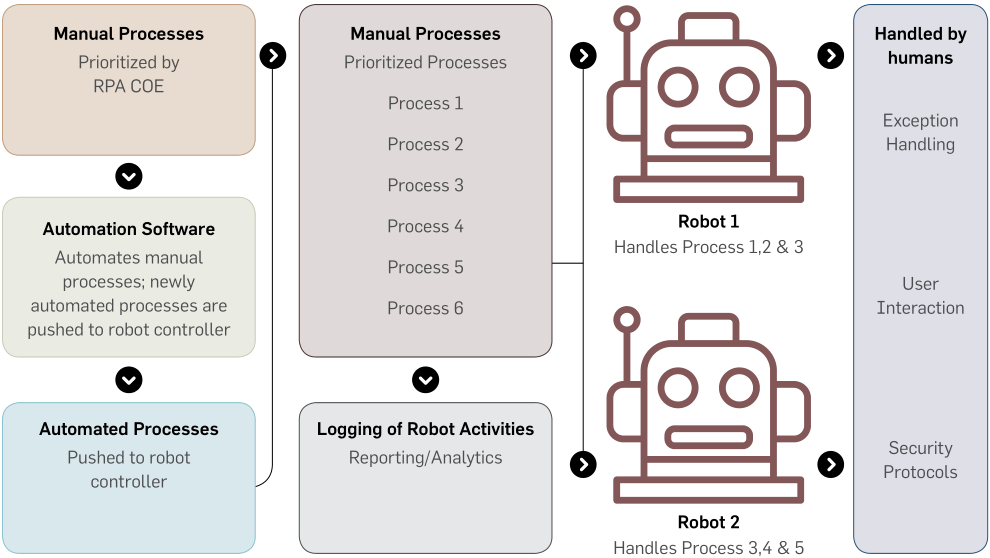
Processes: Vendor and Material Management
Greenko operates with SAP and found that processing vendor
and material master record through the system required a
large number of manual interventions, in terms of validating
data, checking duplication in system and data completeness in
requested format. Waiting time for business users, for vendor
and material code were also high and volumes of this activity
were significantly larger.
After implementing robotic processes automation, vendor
and material creation, extension and validation is quick and
satisfactory. With process automation, the company has
achieved measurable benefits.
Key benefits achieved
- Around 65% to 75% of the time used for manual work has
been reduced
- 100% Processing accuracy, completely eliminating human
errors
- Wait time for employees significantly reduced to 60%
- Support time has increased to 75%. After assigning the
task, the system processes the activity 24/7 by balancing
loads.
- Data quality has improved
- Effective Communication to business users on the status
of processes
Processes: Forecasting data update
The Company needed to update the generated
energy into SLDC (State load despatch
centers) in a timely manner and it required
a lot of manual interaction. The reconciled
data had to be updated in the system and
the process was time consuming, tedious,
and occasionally had errors due to manual
involvement.
After
implementing
Robotic
Processes
Automation,
reconciled
generated
units
statement updating is quick and satisfactory.
Value Created
- 100% processing accuracy by completely
eliminating human errors and the quality
and speed of processes have improved.
- 80% TAT (Tourn around time) reduction
achieved.
- Forecasting data punching for KA, TN, MP
has been completed.

Challenges Faced
Lack of skilled resources: With the growing popularity of RPA, the demand for
skilled resources have been on the rise. RPA deployment can hit a roadblock
in the absence of skilled resources as its success relies heavily on hiring the
right resource.
End-to-end Automation: Sometimes there are processes that cannot be
completely automated with RPA. These processes require the use of Machine
Learning algorithms, which can be an added cost to the company and the
project.
Proper team structure: One of the biggest challenges of RPA implementation
is a proper team structure where resources are shared between teams and
proper processes are defined for smooth operation.
Wrong use-cases for automation: Identifying wrong use cases for automation
is a common mistake that challenges RPA implementation and results in lower
ROI. As a result, it is important to make a case for a proof of concept before
taking the leap of faith.
Unclear expectations: Not knowing the expectations of the team, management
and other stakeholders involved in the RPA implementation can hamper
its progress. Without a clear goal, it is difficult to measure the success of
technology.
Siloed implementation: Teams working in silos can risk crossing wires with the
IT architecture, security, and infrastructure, and this can potentially exclude
them from the corporate disaster recovery plan.
Inconsistent outcomes: Lack of controls and tracking mechanisms for the
automated processes can result in inconsistent outcomes, which can jeopardize
the possibility of scaling RPA.
Technical ambiguity: Sometimes RPA deployment doesn’t lead to expected
results due to ambiguity among the technical staff. When people fail to
ask important questions related to operating requirements during the
implementation, then the automation deployment can go for a toss.
Wrong platform: One of the top challenges of RPA implementation is choosing
the wrong platform due to a lack of knowledge of all the processes. Sometimes,
the deciding factor is the cost, which can result in companies choosing a
platform that doesn’t suit their business needs.
Technological barriers: For RPA implementation, the bot needs to interact
with the Web to read captcha and detect network or browser speed. Without
synchronous management of data, errors may occur.

Value Creation Story:
Automation of Audit Management
Location: HYDERABAD
Overview
At Greenko, establishing, planning, implementing and maintaining the audit management was a challenging task, considering
the number of Plants, Projects and Functions involved. Hence Greenko has taken an initiative to digitize and automate the audit
management process for effective control, easy retrieval of data and greater accuracy.
In alignment with Greenko’s Vision of Digitalization, GIMS with support of ICT team has developed the Greenko Audit
Management Application (GAMA) to bring an integrated approach to the auditing process as a platform for all Operational Plants,
Projects and Corporate Office Functions.
All functions of Greenko undergoing audits and IMS internal auditors shall be provided access to GAMA
application through individual intranet login credentials.
GAMA is designed to be an interactive application and supports the Management Vision and helps the Auditors and auditees to
schedule, prepare and submit Audit findings, Root Cause Analysis and Corrective Actions.

Key Achievements
-
User friendly
-
Easy retrieval of audit management data
-
Ease of audit planning, scheduling and reporting
-
Maintain history of audits at single source
-
Effective monitoring of audit management activities
-
Notifications/Alerts to Auditees and Auditors
Impact & Value Created
Improvement in planning, scheduling and retrieval of data
Challenges
Create
awareness
about
GAMA among employees,
covering all plants and co
functions
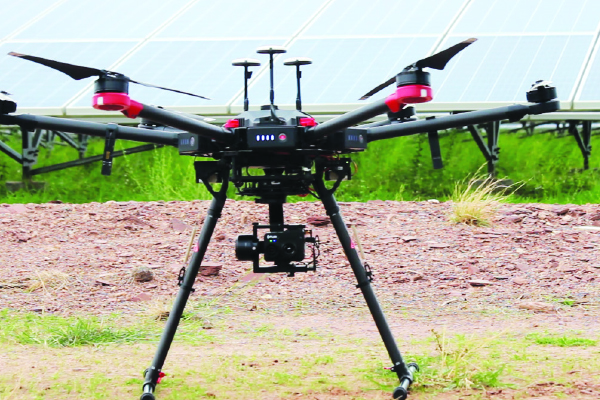
Assuring Optimum Performance with AI-Powered Drones
As Greenko is moving towards deeper decarbonization, the
installation of renewable energy technologies like solar
photovoltaic (PV), wind, and hydro are going to increase, thus
creating the need for regular monitoring of all assets to ensure
reliability and optimum performance.
Greenko has leveraged the advanced technology of unmanned
aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones. The Artificial
Intelligence (AI) powered drones provide comprehensive
coverage, enhanced visibility, site safety, scalability, and
improved operational excellence. The drones also assist in
predictive and adaptive operations and maintenance (O&M) by
providing real-time information.
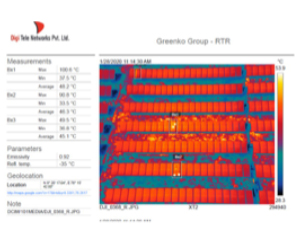
Solar PV power plants require regular monitoring to assure
optimum performance. Drone technology for solar PV system
inspection ensures more accuracy and saves significant time
in comparison to manual inspections. In the case of manual
inspection, a handheld thermal camera is used to detect faults
and issues in operations. This can be a time-consuming process
and could lead to inconsistencies and unavoidable errors in
the inspection data. Greenko has, therefore, replaced manual
inspections with automated inspections that use drones equipped
with a thermal camera. This has helped in reducing the O&M
time, improved accuracy and quality of the recorded data.
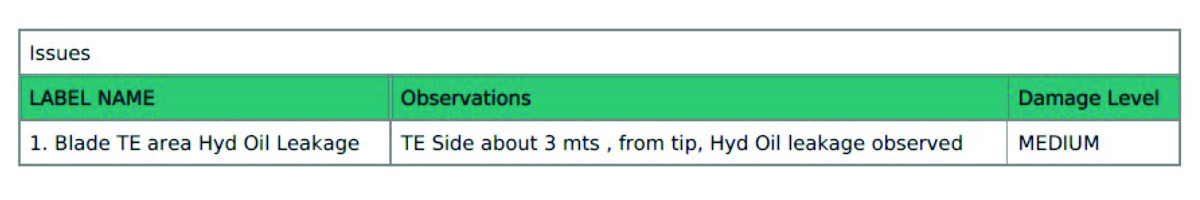
Also, the operational efficiency of the wind power plant can be
affected if the wind turbine generators, gearboxes, and blades
develop cracks, fissures, and other structural issues over
time. Thus, it requires regular inspection to ensure optimum
performance of the wind power plant. Earlier detecting these
issues and defects were not only time consuming but, was also
an expensive affair. Due to the adoption of drone-based aerial
inspection using thermal imaging, the entire monitoring process
has improved in terms of accuracy, quality, and efficiency.
The drone-based aerial inspection involves:
- Planning and Acquiring Data to create flight plans, position
field teams, and operate drones to collect thermal imagery
and record the necessary data using artificial intelligence.
- Process Data using data analytics algorithms to analyze
and validate the inspection data to ensure accuracy and
quality of the recorded data,
- Actionable Insights derived from the reports are delivered
to GAM operations/Project Hub for further action/follow-
up at sites.