 We continued with our pursuit of mitigating impacts through positive
compliance and adherence to ESIA and ESMP; and restoring nature through
habitat restoration at our sites. We also undertook conservation efforts in
partnerships with WWF and the Forest Departments. As the physical impacts
of climate change are becoming more visible through frequent occurrence of
extreme weather conditions and increase in severity of such incidences, we
have undertaken climate risk assessment of some sites and have identified the
mitigation measures to address these risks. Considering that these physical
climatic changes are uncertain, we are considering improving the asset agility
through digitalization as the first defence.
We continued with our pursuit of mitigating impacts through positive
compliance and adherence to ESIA and ESMP; and restoring nature through
habitat restoration at our sites. We also undertook conservation efforts in
partnerships with WWF and the Forest Departments. As the physical impacts
of climate change are becoming more visible through frequent occurrence of
extreme weather conditions and increase in severity of such incidences, we
have undertaken climate risk assessment of some sites and have identified the
mitigation measures to address these risks. Considering that these physical
climatic changes are uncertain, we are considering improving the asset agility
through digitalization as the first defence.
AVP, GIMS
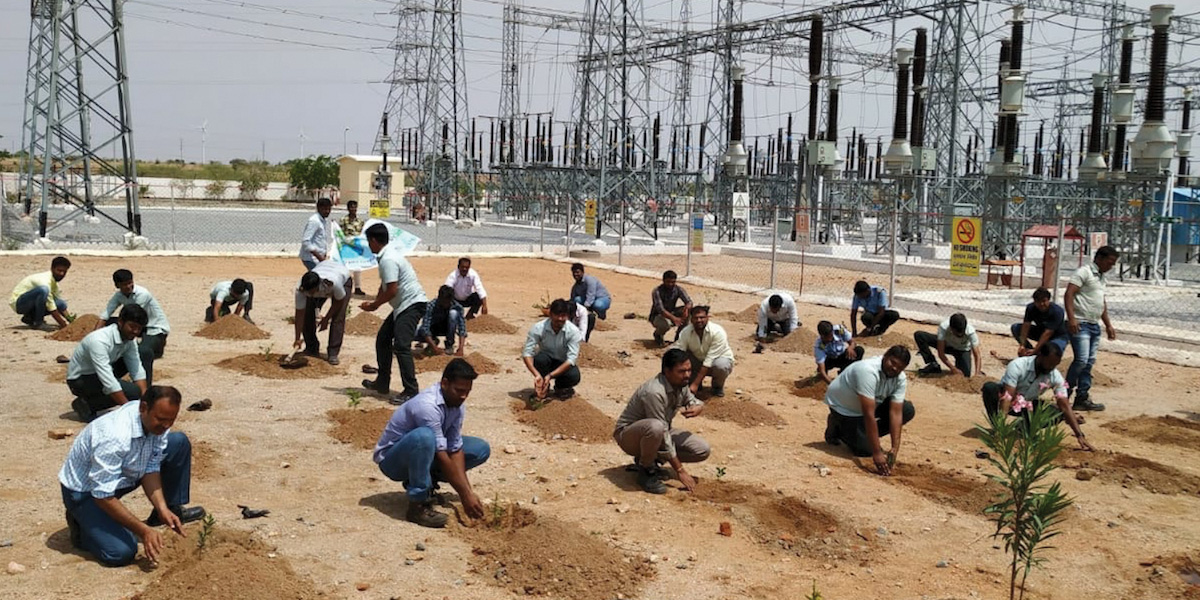

World Environment Day celebrations
Across all sites, Natural Capital considerations (air, water, and soil) and climate change issues are integrated into Greenko’s decision-making at all stages: i.e. design stage, operation stage, and above all, the way it deals with the external world. Greenko’s focus on life cycle has become more relevant and extension of life, second life, and end of life has been integrated into asset management and project planning and execution. The impacts of physical climate change are being identified, mitigated, and managed. Every department, functions, specifically project and asset management teams, contribute actively to caring for the environment. The annual Review of Greenko’s performance during the reporting period demonstrates the continuing efforts in minimizing the use of resources and generation of waste. Going forward, Greenko has set short-term and long-term targets for protecting and enhancing Natural Capital.
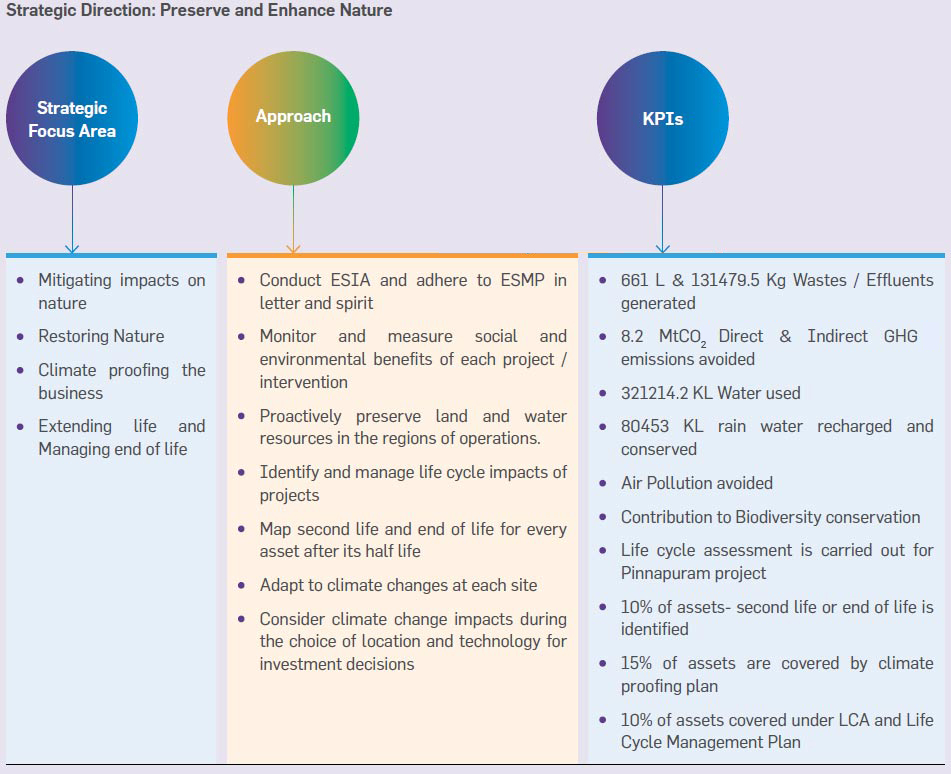
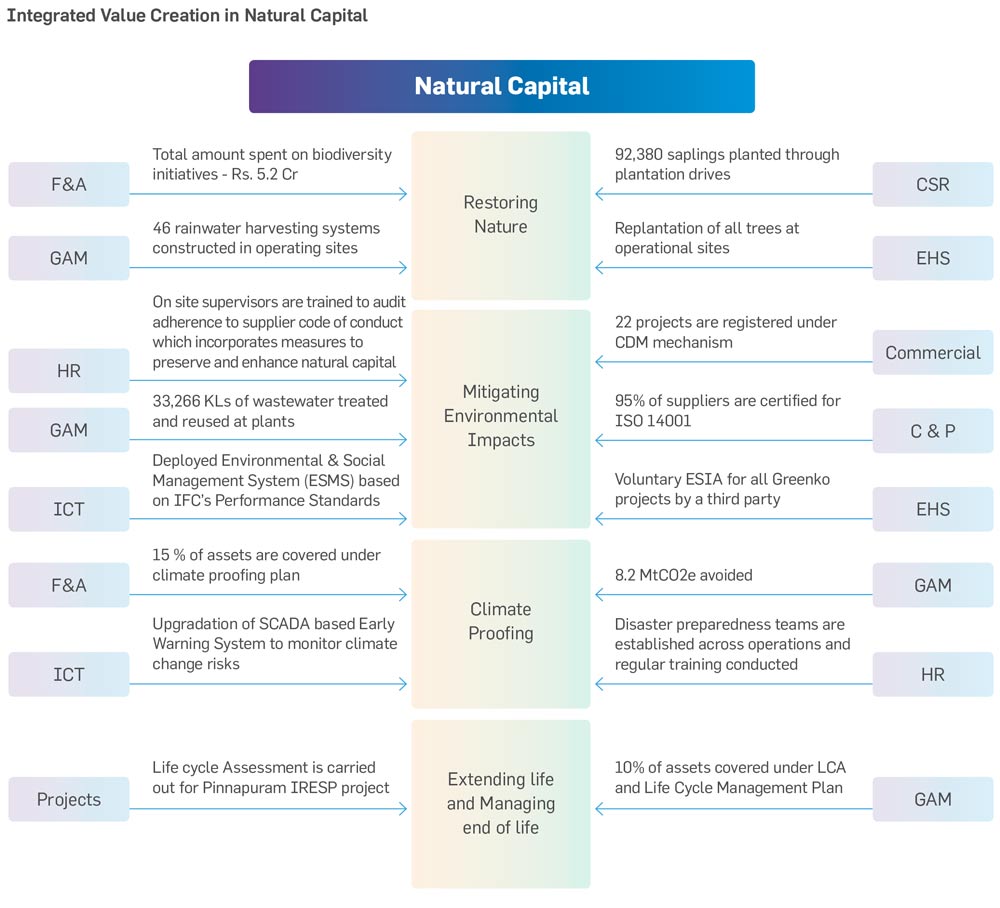
Greenko has identified aspects of its business that impact the environment, the risk they pose to the Company’s business, and the opportunities they offer. Greenko’s business is designed to harness the opportunities in the transition to sustainable development. The organization has carefully designed programs to manage the impacts on the environment. Climate action and management of energy, water, and waste are the key elements of its environmental sustainability program across its operations. Greenko has undertaken various projects and contributes to the conservation of terrestrial ecosystems at their sites, recharges and reuses water, conserves soil and natural drains.
Greenko understands and believes that timely and sufficient availability of natural resources is imperative for the continuity of business operations. Greenko has been proactively working towards preservation and conservation of nature in and around its operations and elsewhere in eco sensitive zones and habitats of threatened species.
Greenko assesses the environmental impact of its projects at the planning stage for promoting broader mitigation and conservation strategies. The Company has endeavoured to understand the direct and indirect impact of its activities and focus on efforts to streamline its operations most efficiently. Greenko carries out an Environmental and Social Impact Assessment (ESIA) study prior to the project development, in line with the requirements of ten Equator Principles; eight International Finance Corporation (IFC) Social & Environmental Sustainability Performance Standards (PS); and IFC Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) Guidelines. All new projects developed by Greenko have undergone ESIA to proactively mitigate any issue that adversely impacts natural capital. All impact mitigation measures in ESMP, which have arisen out of this voluntary ESIA, have been taken up for implementation. Further, Greenko has implem
The Company works towards procuring green alternatives from the suppliers, continuously engaging with the suppliers actively through green procurement initiatives. Greenko is also committed to adopting a procurement process that adopts Ethical, Environmental, and Social principles.
Further, green procurement initiatives help Greenko in preparing for the future regulatory environment and long-term cost-saving opportunities.
Creating awareness in vendors/ suppliers on environmentally preferred goods and services
Making at least 95% of critical suppliers ISO 14001 certified and RoHS compliant by March 2024
Inclusion of environmental specifications and evaluation criteria as per emerging technologies in centrally managed procurement
Developing a collaborative approach to optimise information-sharing, consistency and performance measurement and Life-cycle analysis
During the FY 2019-20, Greenko made significant procurement of Green Alternatives and initiatives
These initiatives combined with planning the transport for consolidating packages by the vendors have significantly reduced the scope of 1&2 GHG emissions up to 50%. Internal movement of the vehicle from the warehouse to the Flight loading area is also monitored to achieve and maintain the outcome of GHG emissions reductions. Greenko also ensured that its major suppliers (95% in all) are upgraded to ISO 14001 certification and are RoHS compliant.
Greenko recognizes the fact, that climate change is an important issue that can significantly affect the lives and health of various stakeholders. Extreme weather conditions leading to natural disasters like strong and frequent storms can adversely affect the supply of power and damage generation and grid infrastructure.
Greenko has avoided 8.2 million tons of CO2 emission by generating clean energy. In addition, the group has, till date, registered 22 Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) projects with UNFCCC.
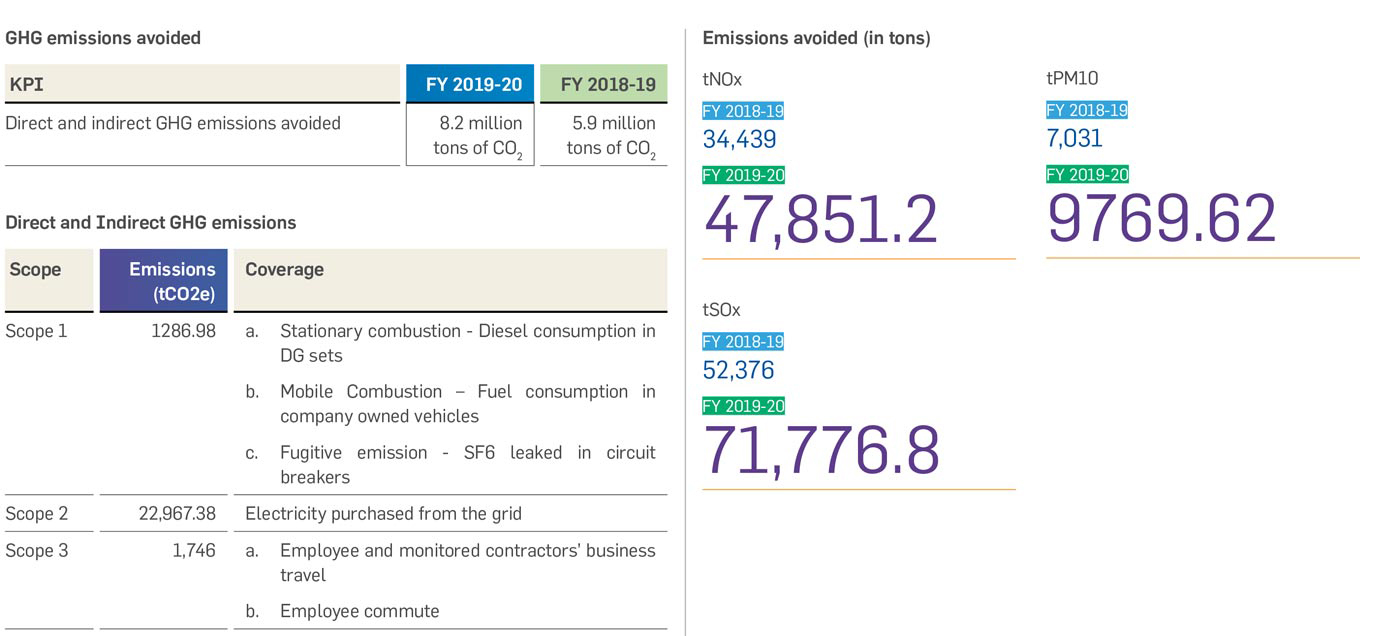
For more details on Greenko’s GHG emissions and inventory standards used please refer Greenko’s GHG Accounting Manual
Greenko is committed to continually improve its Waste management practices at all of its facilities. The Company’s waste management adheres to the principles in Environment and Social Management System. The ESMS requires conformance to legal requirements along with reduction in waste generation through reuse or recycle, whenever possible.
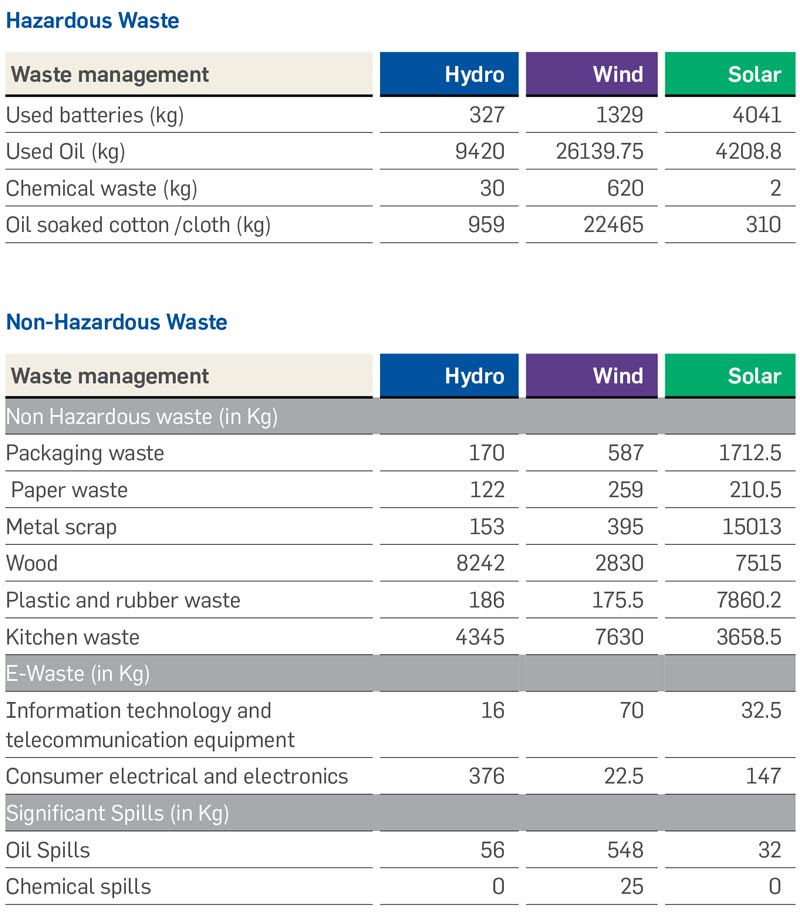
Wind, solar and hydro projects do not consume any fuel for power generation. Thus, the material consumption in these plants is only towards the O&M of plants.
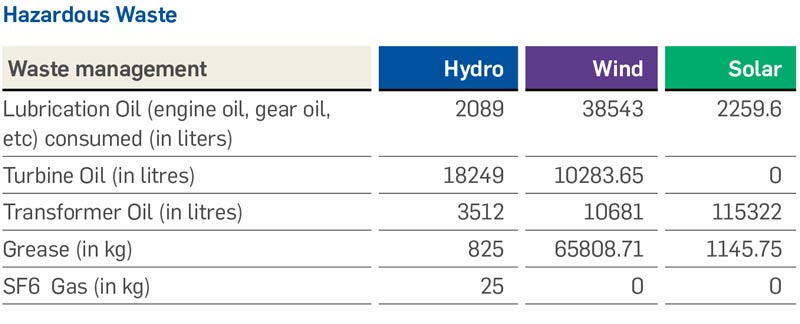
Greenko carries out its waste management program with the help of an authorised third-party, which involves monitoring garbage collection, segregation and disposal of all the waste generated at the operating premises. Some are sold to authorised recyclers and some to hazardous waste treatment facilities and some others are landfilled.
Greenko continues to monitor and reduce its freshwater usage, as operations have a significant impact on the withdrawal or discharge of water in the regions where it operates. The main uses of water are for cleaning solar modules, construction activities, domestic use, and biodiversity purposes. At all sites, Greenko diligently does rain water harvesting, adopts drip or sprinkler irrigation and water conservation measures in cleaning.
Greenko constructed 22 check dams without disturbing the natural drains. It also helped with 12 km of ground water table recharge canal augmentation which were routed to a reservoir. This harvested rainwater is being used for module cleaning purposes. A pond has been excavated at plant area to divert rainwater and store hte water being used for module cleaning and plantation. The capacity of the Reservoir is 4,00,000 KL. Its major benefit was improvement of ground water table by adopting check dams, canal augmentation, rainwater harvesting etc.

Reservoir and check Dam construction at ghani solar park
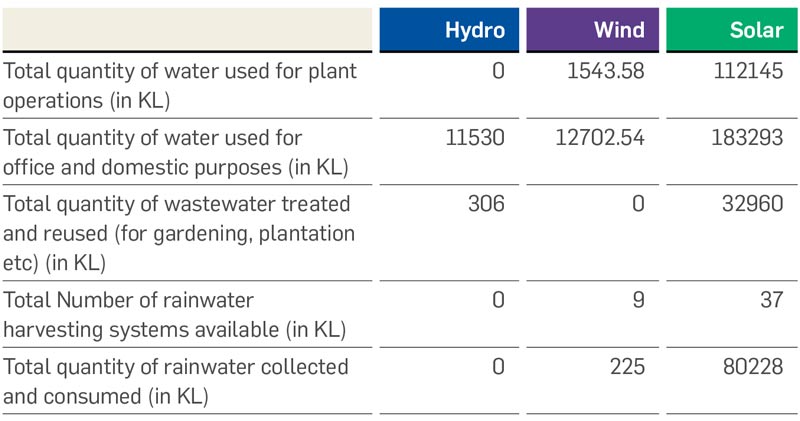
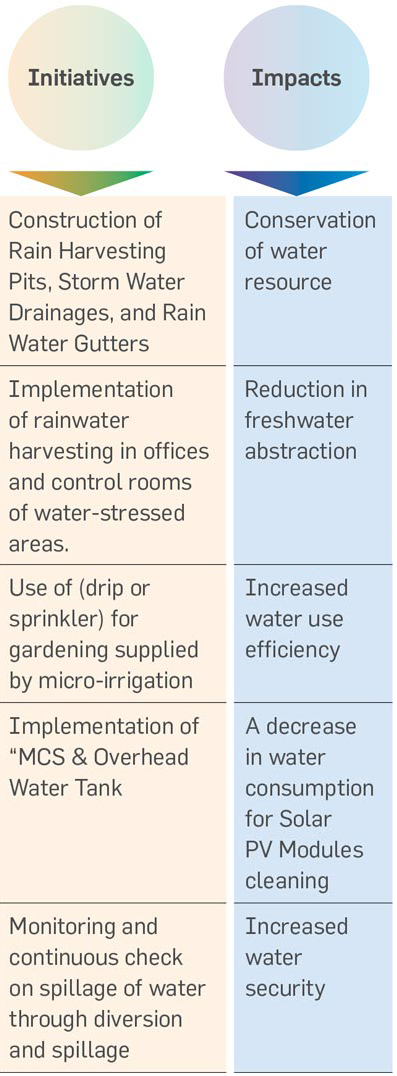
While adopting new technology, the Company evaluates and considers its feasibility, considering water efficiency as one of the critical deciding factors. Greenko owns and occupies significant area through which natural drainage flow, water recharge and storage is carried out. It manages the drainage flow in such a way that it harnesses the water resource first for the use of the community and then for its own purposes. At many sites, it has managed regional level watershed development and enhanced water availability in the region.
Greenko has undertaken multiple initiatives for energy efficiency at its operating locations which are enlisted below:

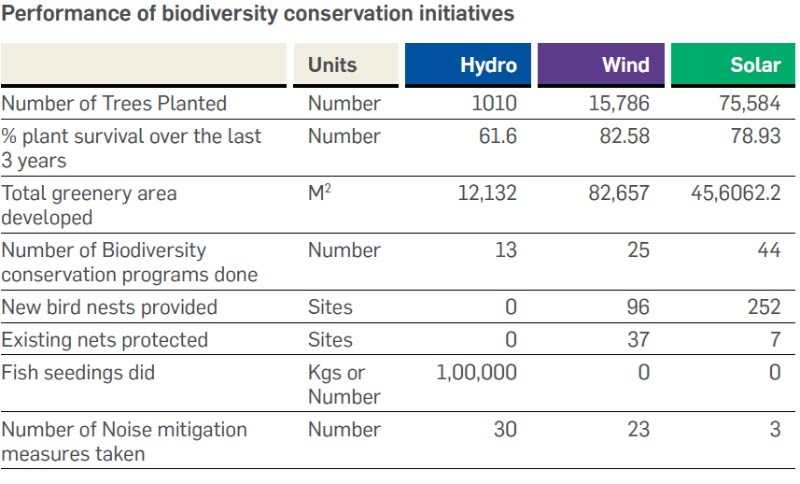
Greenko is committed to design and implement projects based on extensive Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). The company brings the best efforts to avoid setting up its operations that have potential impacts on biodiversity. Further, Greenko takes proactive measures to restore, protect, and enhance biodiversity. The projects undertaken by Greenko in this direction comprises of habitat conservation, natural or sustainable farming, protecting sea-based wildlife systems, fish seeding initiatives. Further to this, there is an extensive activity of tree plantation at all its operation sites. In pursuance of commitment towards Biodiversity Conservation and Sustainable Management of Living Natural Resources, Greenko is supporting various projects in various areas.
Greenko understands the role of plantation in protecting their sites and enhancing the productivity of its operating resource from soil bonding to minimizing impacts of natural disasters, rainfalls, etc.

Renewable energy has proven to be a key in the transition towards a low carbon future and to meet the 2 °C climate goal, thus minimizing the catastrophic impacts of climate change as well as addressing the growing energy demand. However, like every other sector, renewables are also susceptible to the impacts of the changing climate.
Greenko has conducted Climate Risk Assessment and Management as part of its decision-making system, with an aim to make informed choices, building capacity, planning, and prioritizing mitigation and adaptation measures to reduce its vulnerability to climate change. In this view, Greenko has integrated the climate risk assessment and management aspect in its existing risk management framework, to proactively and systematically identify and analyse potential climate-related hazards to Greenko’s operations, based on historical events, trends, forecasts, and projections.
In this context, Greenko has assessed the impact of physical risks across different stages of its operating lifecycle, such as,
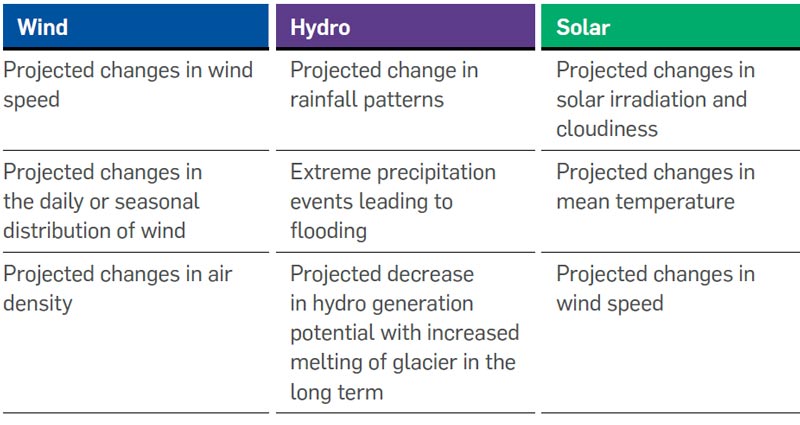
In this context, Greenko has conducted a climate risk assessment for six of its critical operating sites to assess and manage climate risk vulnerability of assets and its productivity. The six sites are as follows,
Greenko has studied projected climate change impacts on its operations using IPCC’s RCP 4.5 scenario which is the low-medium emission pathway (equivalent to 1.7-3.2°C temperature increase). The climate change projections were studied for the period of 2020-2039 (Short term) and 2040- 2059 (Medium Term).
The climate risk assessment reveals that the transition risks are already well addressed by Greenko. The physical risk for operations related increased heat stress will be mitigated through water conservation and harvesting measures. The physical impacts on resource availability viz., wind pattern, solar radiation and hydrological flows is to be addressed through agility and predictive and adaptive capabilities through Digitalization.
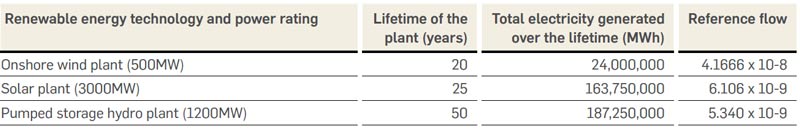
A Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) was conducted for an onshore 500MW wind plant, 3000MW solar and 1200MW pumped storage hydro plant as part of Greenko’s Integrated Renewable Energy Project (IRESP) according to the ISO 14040 and 14044 standards. An LCA is usually conducted for analysing the environmental impact of a product/system across the various The results are presented as per two different scenarios i.e., the baseline scenario and after adjusting the storage function of the plant scenario. Baseline scenario: The graph below shows the overall potential environmental impacts of a 500MW wind plant consisting of 250 turbines (with a rating of 2MW per turbine), a 3000MW solar plant consisting of 3749991 solar panels, 500 inverters and a 1200MW pumped storage hydro plant, covering the entire lifecycle of the respective power plant, per MWh of electricity generated. Reference flows for Greenko’s renewable energy technologies stages of its lifecycle. In this case, the goal of the LCA study is to analyse the environmental impacts associated with the production of electricity from Greenko’s different renewable energy technologies i.e., onshore wind plant, solar plant and a pumped storage hydro plant and explore the consequence of extension of life and end of life management. A process-based LCA approach was utilized for this study.
A cradle-grave LCA study was conducted i.e., the environmental impacts are calculated over the entire lifecycle of the renewable energy technology plants involving the extraction of raw materials, manufacturing of the components, assembling, transport, operation, maintenance and end-of-life treatment. The functional unit for this LCA study was defined as 1MWh of electricity generated by the corresponding renewable energy technology plant. The lifetime of the onshore wind plant, solar plant and pumped storage hydro plant was assumed to be 20, 25 and 50 years respectively. The reference flows for Greenko’s renewable energy technologies are as follows:
The results are presented as per two different scenarios i.e., the baseline scenario and after adjusting the storage function of the plant scenario.
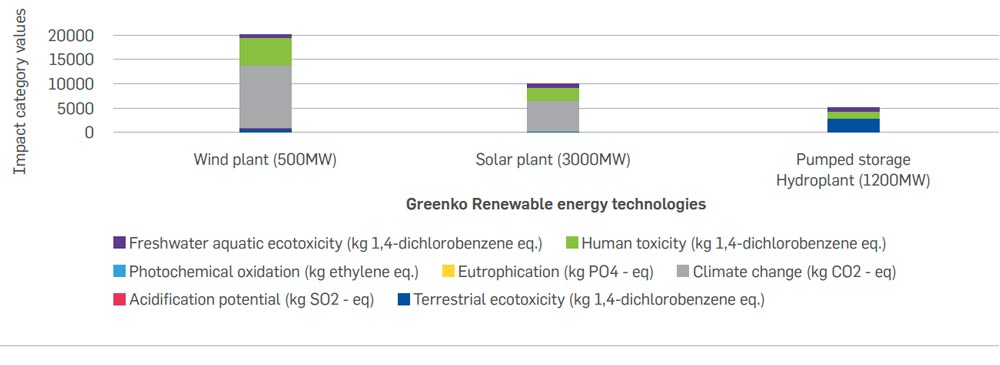
The graph below shows the overall potential environmental impacts of a 500MW wind plant consisting of 250 turbines (with a rating of 2MW per turbine), a 3000MW solar plant consisting of 3749991 solar panels, 500 inverters and a 1200MW pumped storage hydro plant, covering the entire lifecycle of the respective power plant, per MWh of electricity generated.
From the above figure, it can be seen that the onshore wind plant has the highest impact followed by the pumped storage hydro plant and solar plant. The lifecycle stage impacts for the respective plants are discussed more in detail below.
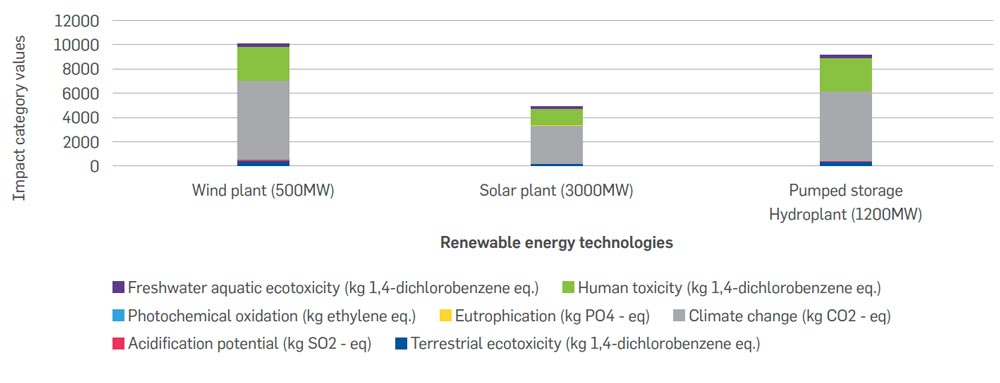
The below figure represents the potential environmental impacts of raw material and component production, use and maintenance and disposal stages of the lifecycle of the onshore wind plant. The graph shows that the component production and end-of-life treatment stages contribute the most towards the environmental impact of the wind plant. The results show that for the wind plant components, the site cables and turbine contribute most significantly to the environmental impact categories. Similarly, the disposal stage contributes to at least 50% of the total environmental impact of the wind plant. This is due to the reason that after usage, as part of the end-of-life treatment, the majority of the raw materials (around 70%) used in the various components of the wind plant are landfilled and it results in a higher impact in the disposal stage.
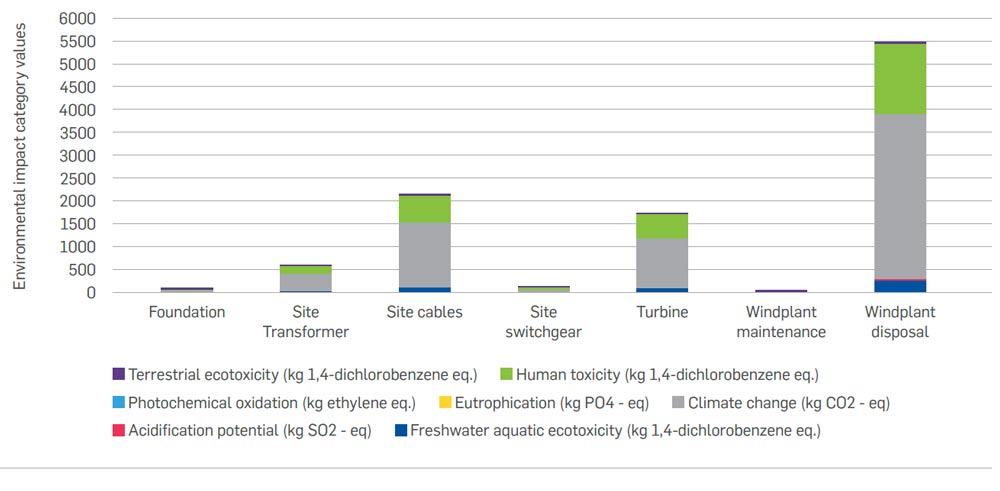
The below figure represents the potential environmental impacts for raw material and component production, use and maintenance and disposal stages of the lifecycle of the solar plant. The graph shows that the component production and end-oflife treatment stages contribute the most towards the environmental impact of the solar plant. Of the solar plant components, the solar inverter contributes the most towards the environmental impact categories. Similarly, the disposal stage contributes to around 20% of the overall environmental impact of the solar plant. This is due to the reason that after usage, as part of the endof- life treatment, the majority of the raw materials (around 70%) used in the various components of the solar plant are landfilled and it results in a higher impact at the disposal stage.
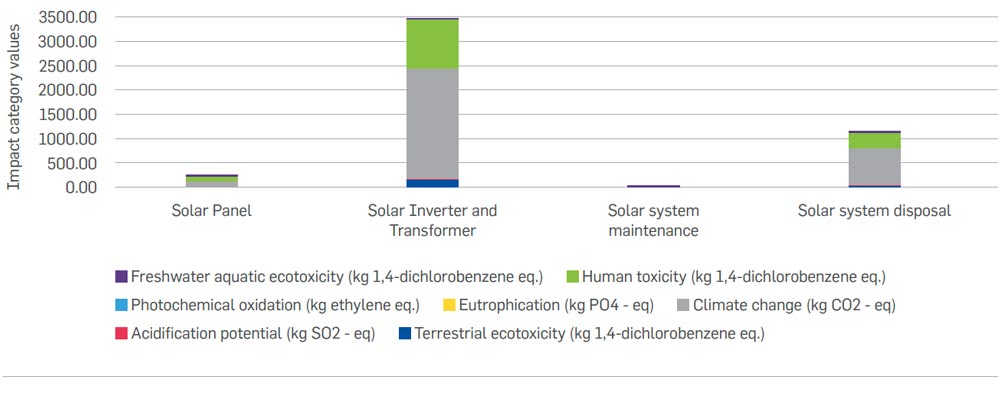
The below figure represents the potential environmental impacts for raw material and component production, use and maintenance and disposal stages of the lifecycle of the pumped storage hydro plant. The graph shows that the component production and end-of-life treatment stages contribute the most towards the environmental impact of the pumped storage hydro plant. Of the pumped storage hydro plant components, the reversible Francis turbine contributes the most towards the environmental impact categories. Similarly, the disposal stage contributes to more than 90% of the overall environmental impact of the hydro plant. This is due to the reason that after usage, as part of the end-of-life treatment, the majority of the raw materials (around 70%) used in the various components of the pumped storage hydro plant are landfilled which results in a higher impact in the disposal stage.
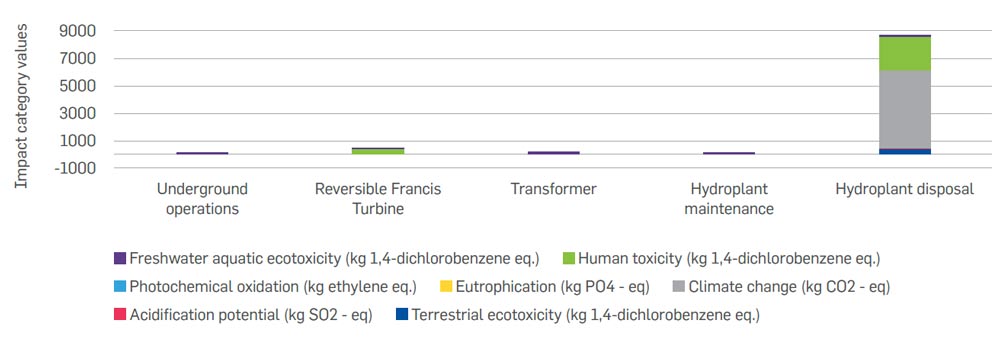
The below figure shows the environmental impacts per MWh of renewable energy technologies after adjusting the storage function of the hydro, solar and wind plant. The pumped storage hydro plant has a much lower impact than the wind and solar plants because the pumped hydro plant will generate more energy from its storage during its entire lifecycle than the wind and solar plants. This energy stored in the storage system will be generated during the period of high demand, which will result in more electricity generation by the hydro plant, from storage and therefore reduce the energy generation of solar and wind plants across its lifecycle.
A sensitivity analysis is conducted to test the robustness of the LCA results and it provides an evaluation of the underlying assumptions and choices made for the LCA, which aims to provide an understanding and importance of these choices. In this study, a sensitivity analysis was performed by varying the lifetimes of the wind, solar and pumped storage hydro plant. The results are provided separately according to both the baseline scenario and after adjusting for the storage function scenarios of the power plant.
The lifetimes of the wind, solar and pumped storage hydro plant are designed for 20, 25 and 50 years respectively. However, this may vary according to the specific operating conditions of the plant. The power plant lifetime is an important assumption in the LCA because the environmental impacts are calculated over the lifetime of the plant, for every MWh of electricity generated. As such, the changes in the lifetime of the plant could have a substantial overall effect on the impacts produced by the corresponding power plant.
The below graph represents the sensitivity analysis results, when the lifetimes of the wind, solar plant were increased to 50 years each and the pumped storage hydro plant’s life was increased to 100 years respectively in comparison to the baseline scenario results. The graph shows that the overall potential environmental impacts decrease by at least 50% when the lifetimes of the wind, solar and pumped storage hydro plants are increased to 50, 50 and 100 years respectively. Therefore, the results imply that the impacts per MWh directly correspond to the specific power plant’s lifetime.
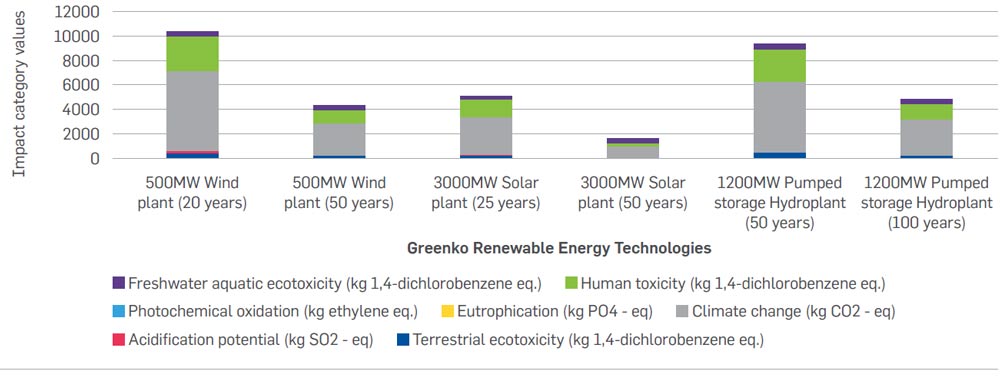
The below graph shows the results of the wind, solar and pumped storage hydro plant whose lifetimes have been increased to 50, 50 and 100 years respectively after adjusting for the storage function in comparison to the original results. Similar to the above graph, the overall potential impacts decrease by at least 50%, when the lifetimes of the wind, solar and pumped storage hydro plants are increased to 50, 50 and 100 years respectively, after adjusting for the storage function.
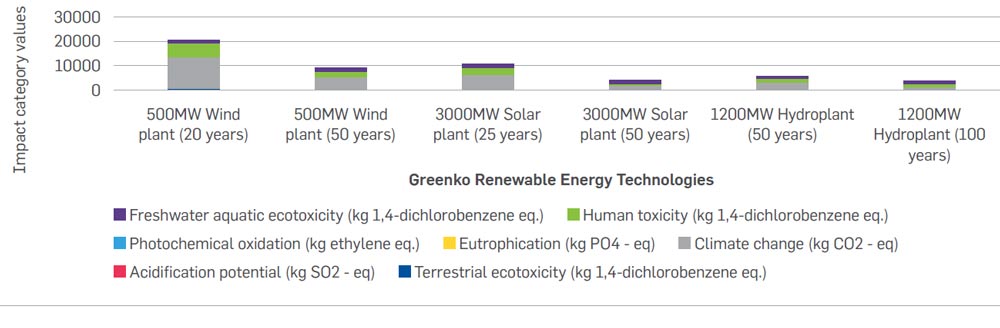
Thus, from the LCA study, it can be understood that the production and disposal stages contribute the most towards the environmental impacts of the onshore wind, solar and pumped storage hydro plants. Although nothing much can be done by Greenko with respect to the production of the raw materials and components used in the plants, some measures can be taken by Greenko to ensure the proper recycling and reuse of raw materials used in the various components of the different renewable energy technology plants after usage and ensure that the raw materials doesn’t end up in landfills. A sensitivity analysis was also conducted to understand the influence of the varying lifetimes on the overall environmental impacts of the power plants.
Overall, the study represents a robust and good reflection of the potential environmental impacts of Greenko’s onshore 500MW wind plant, 3000MW solar plant and 1200MW pumped storage hydro plant. The LCA is based upon accurate product knowledge and current state-of-the-art technology used in the LCA field, both in terms of methodologies used and datasets used to account environmental impacts as well as the LCA tools and software applied.
Earth Hour at Greenko focused on enhancing awareness on biodiversity loss. Greenko joined hands with millions of people across the globe, to switch off lights at the business premise with a commitment to:
Greenko is a responsible employer, cultivates consciousness towards its employees to participate in corporate volunteer programs.
Greenko has participated in the United Way INDIA PLOG RUN as a tribute to the Father of the Nation Mahatma Gandhi on his 150th birth anniversary.
World Water Day is an annual UN observance day (22 March) that highlights the importance of freshwater. Greenko celebrated this with high enthusiasm and committed itself to preserve natural resources.
At Greenko, sustainability is the very foundation of our business. In our operations, we endeavour to integrate biodiversity and environmental protection. Since inception Greenko has been celebrating World Environment Day by conducting many programs on the conservation and protection of biodiversity.
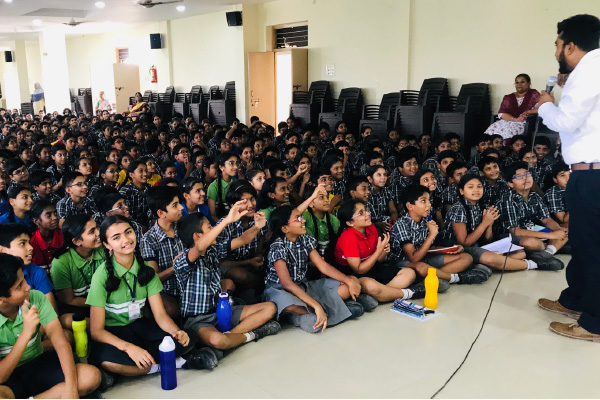

Employee Volunteering with WWF for Earth Hour at Hyderabad Schools
Sanctuary Nature Foundation, sponsored by DSP Mutual Fund and IndusInd Bank and supported by Greenko, presented the 20th Sanctuary Wildlife Awards at the National Centre for the Performing Arts (NCPA) in Mumbai on December 24, 2019. The Sanctuary Wildlife Awards were instituted in the year 2000 and over the last two decades, we have been honoured to recognize these Earth Heroes, to shine a light on their work, and express our gratitude for their selfless work.
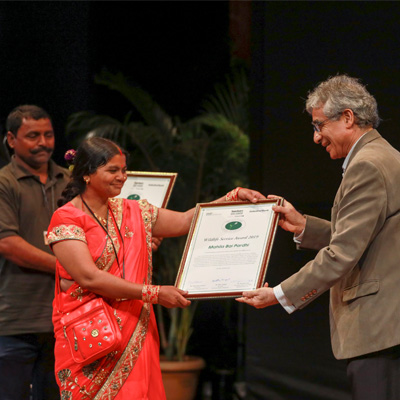

The Sanctuary Wildlife Award-2019

Greenko is committed to ensuring the long-term survival of the endangered species Red Panda in Sikkim state of the eastern Himalayas.